Targeting the SR-B1 Receptor as a Gateway for Cancer Therapy and Imaging
- PMID: 28018216
- PMCID: PMC5156841
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2016.00466
Targeting the SR-B1 Receptor as a Gateway for Cancer Therapy and Imaging
Abstract
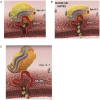
Malignant tumors display remarkable heterogeneity to the extent that even at the same tissue site different types of cells with varying genetic background may be found. In contrast, a relatively consistent marker the scavenger receptor type B1 (SR-B1) has been found to be consistently overexpressed by most tumor cells. Scavenger Receptor Class B Type I (SR-BI) is a high density lipoprotein (HDL) receptor that facilitates the uptake of cholesterol esters from circulating lipoproteins. Additional findings suggest a critical role for SR-BI in cholesterol metabolism, signaling, motility, and proliferation of cancer cells and thus a potential major impact in carcinogenesis and metastasis. Recent findings indicate that the level of SR-BI expression correlate with aggressiveness and poor survival in breast and prostate cancer. Moreover, genomic data show that depending on the type of cancer, high or low SR-BI expression may promote poor survival. This review discusses the importance of SR-BI as a diagnostic as well as prognostic indicator of cancer to help elucidate the contributions of this protein to cancer development, progression, and survival. In addition, the SR-B1 receptor has been shown to serve as a potential gateway for the delivery of therapeutic agents when reconstituted high density lipoprotein nanoparticles are used for their transport to cancer cells and tumors. Opportunities for the development of new technologies, particularly in the areas of cancer therapy and tumor imaging are discussed.
Keywords: Drug Delivery Systems; SR-B1; gateway for theranostics; individual therapy; tumor imaging.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

