Acetylcholine-Induced Inhibition of Presynaptic Calcium Signals and Transmitter Release in the Frog Neuromuscular Junction
- PMID: 28018246
- PMCID: PMC5149534
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2016.00621
Acetylcholine-Induced Inhibition of Presynaptic Calcium Signals and Transmitter Release in the Frog Neuromuscular Junction
Abstract
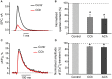
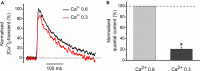
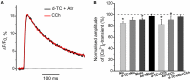
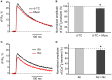
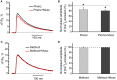
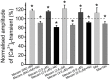
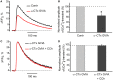
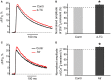
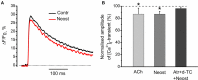
Acetylcholine (ACh), released from axonal terminals of motor neurons in neuromuscular junctions regulates the efficacy of neurotransmission through activation of presynaptic nicotinic and muscarinic autoreceptors. Receptor-mediated presynaptic regulation could reflect either direct action on exocytotic machinery or modulation of Ca2+ entry and resulting intra-terminal Ca2+ dynamics. We have measured free intra-terminal cytosolic Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) using Oregon-Green 488 microfluorimetry, in parallel with voltage-clamp recordings of spontaneous (mEPC) and evoked (EPC) postsynaptic currents in post-junctional skeletal muscle fiber. Activation of presynaptic muscarinic and nicotinic receptors with exogenous acetylcholine and its non-hydrolized analog carbachol reduced amplitude of the intra-terminal [Ca2+]i transients and decreased quantal content (calculated by dividing the area under EPC curve by the area under mEPC curve). Pharmacological analysis revealed the role of muscarinic receptors of M2 subtype as well as d-tubocurarine-sensitive nicotinic receptor in presynaptic modulation of [Ca2+]i transients. Modulation of synaptic transmission efficacy by ACh receptors was completely eliminated by pharmacological inhibition of N-type Ca2+ channels. We conclude that ACh receptor-mediated reduction of Ca2+ entry into the nerve terminal through N-type Ca2+ channels represents one of possible mechanism of presynaptic modulation in frog neuromuscular junction.
Keywords: N-type Ca channels; calcium transient; muscarinic receptors; neuromuscular synapse; nicotinic receptors; presynaptic acetylcholine receptors; quantum secretion of acetylcholine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Presynaptic Acetylcholine Receptors Modulate the Time Course of Action Potential-Evoked Acetylcholine Quanta Secretion at Neuromuscular Junctions.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 22;10(8):1771. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081771. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35892671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscarinic M1 acetylcholine receptors regulate the non-quantal release of acetylcholine in the rat neuromuscular junction via NO-dependent mechanism.J Neurochem. 2007 Sep;102(6):2110-2117. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04696.x. Epub 2007 Jun 11. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17561934
-
Nerve terminal currents induced by autoreception of acetylcholine release.J Neurosci. 1998 Dec 1;18(23):9954-61. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-23-09954.1998. J Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 9822751 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of ACh release by presynaptic muscarinic autoreceptors in the neuromuscular junction of the newborn and adult rat.Eur J Neurosci. 2003 Jan;17(1):119-27. doi: 10.1046/j.1460-9568.2003.02428.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12534975
-
Presynaptic membrane receptors in acetylcholine release modulation in the neuromuscular synapse.J Neurosci Res. 2014 May;92(5):543-54. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23346. Epub 2014 Jan 27. J Neurosci Res. 2014. PMID: 24464361 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of Neuronal Nicotinic Receptors Inhibits Acetylcholine Release in the Neuromuscular Junction by Increasing Ca2+ Flux through Cav1 Channels.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 21;22(16):9031. doi: 10.3390/ijms22169031. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445737 Free PMC article.
-
ATP Reduces the Entry of Calcium Ions into the Nerve Ending by Blocking L-type Calcium Channels.Acta Naturae. 2018 Apr-Jun;10(2):93-96. Acta Naturae. 2018. PMID: 30116620 Free PMC article.
-
The neurotoxicity of Paraquat and its degradation products on drosophila melanogaster.Sci Rep. 2025 May 12;15(1):16447. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86413-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40355491 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons Reveals a Molecular Basis for Vulnerability Within the Ts65Dn Model of Down Syndrome and Alzheimer's Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2021 Oct;58(10):5141-5162. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02453-3. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2021. PMID: 34263425 Free PMC article.
-
Presynaptic Acetylcholine Receptors Modulate the Time Course of Action Potential-Evoked Acetylcholine Quanta Secretion at Neuromuscular Junctions.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 22;10(8):1771. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10081771. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35892671 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ciani S., Edwards C. (1963). The effect of acetylcholine on neuromuscular transmission in the frog. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 142, 21–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

