Differential CCR7 Targeting in Dendritic Cells by Three Naturally Occurring CC-Chemokines
- PMID: 28018341
- PMCID: PMC5145889
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00568
Differential CCR7 Targeting in Dendritic Cells by Three Naturally Occurring CC-Chemokines
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Differential CCR7 Targeting in Dendritic Cells by Three Naturally Occurring CC-Chemokines.Front Immunol. 2017 Feb 8;8:89. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00089. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28179908 Free PMC article.
Abstract
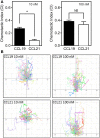
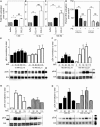
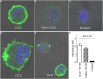
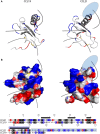
The CCR7 ligands CCL19 and CCL21 are increasingly recognized as functionally different (biased). Using mature human dendritic cells (DCs), we show that CCL19 is more potent than CCL21 in inducing 3D chemotaxis. Intriguingly, CCL21 induces prolonged and more efficient ERK1/2 activation compared with CCL19 and a C-terminal truncated (tailless) CCL21 in DCs. In contrast, tailless-CCL21 displays increased potency in DC chemotaxis compared with native CCL21. Using a CCL21-specific antibody, we show that CCL21, but not tailless-CCL21, accumulates at the cell surface. In addition, removal of sialic acid from the cell surface by neuraminidase treatment impairs ERK1/2 activation by CCL21, but not by CCL19 or tailless-CCL21. Using standard laboratory cell lines, we observe low potency of both CCL21 and tailless-CCL21 in G protein activation and β-arrestin recruitment compared with CCL19, indicating that the tail itself does not improve receptor interaction. Chemokines interact with their receptors in a stepwise manner with ultimate docking of their N-terminus into the main binding pocket. Employing site-directed mutagenesis we identify residues in this pocket of selective CCL21 importance. We also identify a molecular switch in the top of TM7 important for keeping CCR7 in an inactive conformation (Tyr312), as introduction of the chemokine receptor-conserved Glu (or Ala) induces high constitutive activity. Summarized, we show that the interaction of the tail of CCL21 with polysialic acid is needed for strong ERK signaling, whereas it impairs CCL21-mediated chemotaxis and has no impact on receptor docking consistent with the current model of chemokine:receptor interaction. This indicates that future selective pharmacological targeting of CCL19 versus CCL21 should focus on a differential targeting of the main receptor pocket, while selective targeting of tailless-CCL21 versus CCL21 and CCL19 requires targeting of the glycosaminoglycan (GAG) interaction.
Keywords: CCL19; CCL21; CCR7; ERK; biased signaling; dendritic cell; tailless-CCL21.
Figures





References
-
- Bachelerie F, Ben-Baruch A, Burkhardt AM, Combadiere C, Farber JM, Graham GJ, et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. [corrected]. LXXXIX. Update on the extended family of chemokine receptors and introducing a new nomenclature for atypical chemokine receptors. Pharmacol Rev (2014) 66:1–79.10.1124/pr.113.007724 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

