The Capricious Nature of Bacterial Pathogens: Phasevarions and Vaccine Development
- PMID: 28018352
- PMCID: PMC5149525
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00586
The Capricious Nature of Bacterial Pathogens: Phasevarions and Vaccine Development
Abstract
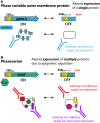
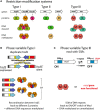
Infectious diseases are a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, and vaccines are one of the most successful and cost-effective tools for disease prevention. One of the key considerations for rational vaccine development is the selection of appropriate antigens. Antigens must induce a protective immune response, and this response should be directed to stably expressed antigens so the target microbe can always be recognized by the immune system. Antigens with variable expression, due to environmental signals or phase variation (i.e., high frequency, random switching of expression), are not ideal vaccine candidates because variable expression could lead to immune evasion. Phase variation is often mediated by the presence of highly mutagenic simple tandem DNA repeats, and genes containing such sequences can be easily identified, and their use as vaccine antigens reconsidered. Recent research has identified phase variably expressed DNA methyltransferases that act as global epigenetic regulators. These phase-variable regulons, known as phasevarions, are associated with altered virulence phenotypes and/or expression of vaccine candidates. As such, genes encoding candidate vaccine antigens that have no obvious mechanism of phase variation may be subject to indirect, epigenetic control as part of a phasevarion. Bioinformatic and experimental studies are required to elucidate the distribution and mechanism of action of these DNA methyltransferases, and most importantly, whether they mediate epigenetic regulation of potential and current vaccine candidates. This process is essential to define the stably expressed antigen target profile of bacterial pathogens and thereby facilitate efficient, rational selection of vaccine antigens.
Keywords: DNA methyltransferase; DNA modification enzyme; epigenetics; gene expression; phase variation; vaccine.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation. The Global Burden of Disease (2004 Update) (2004). Available from: http://www.who.int/healthinfo/global_burden_disease/2004_report_update/en/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

