Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Respond Directly to Apoptotic Cells by Secreting Immune Regulatory IL-10 or IFN-α
- PMID: 28018356
- PMCID: PMC5155015
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00590
Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Respond Directly to Apoptotic Cells by Secreting Immune Regulatory IL-10 or IFN-α
Abstract
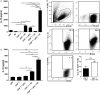
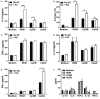
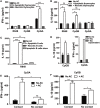
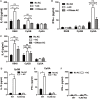
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) play a pivotal role in driving the autoimmune disease systemic lupus erythematosus, via the secretion of IFN-α in response to nuclear self-antigens complexed with autoantibodies. Apoptotic cells, generated at sites of inflammation or secondary lymphoid organs, are exposed to activated pDCs and also express the same nuclear antigens on their cell surface. Here, we show that in the absence of autoantibodies, activated pDCs directly respond to apoptotic cell-expressed chromatin complexes by secreting IL-10 and IL-6, which also induces T cells to secrete IL-10. Conversely, when activated by the viral mimetic CpG-A, apoptotic cells enhance their secretion of IFN-α. This study demonstrates that activated pDCs respond directly to apoptotic cells and may maintain tolerance via IL-10, or promote inflammation through secretion of IFN-α, depending on the inflammatory context.
Keywords: IL-10; apoptosis; apoptotic cell; plasmacytoid dendritic cell; toll-like receptor.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Abnormalities in circulating plasmacytoid dendritic cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(4):R137. doi: 10.1186/ar3075. Epub 2010 Jul 9. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20618924 Free PMC article.
-
Mycophenolic acid, the active form of mycophenolate mofetil, interferes with IRF7 nuclear translocation and type I IFN production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Nov 9;22(1):264. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02356-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 33168076 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 9 suppression in plasmacytoid dendritic cells after IgE-dependent activation is mediated by autocrine TNF-alpha.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008 Feb;121(2):486-91. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.09.049. Epub 2007 Nov 26. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18036648
-
Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells as a New Therapeutic Target for Autoimmune Pancreatitis and IgG4-Related Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 23;12:713779. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.713779. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34367181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions of TGF-β-exposed plasmacytoid dendritic cells.Crit Rev Immunol. 2012;32(6):529-53. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.2013005868. Crit Rev Immunol. 2012. PMID: 23428227 Review.
Cited by
-
Host-virus interaction and viral evasion.Cell Biol Int. 2021 Jun;45(6):1124-1147. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11565. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Cell Biol Int. 2021. PMID: 33533523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptotic Donor Cells in Transplantation.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 25;12:626840. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.626840. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33717145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bleomycin-Induced Lung Injury Increases Resistance to Influenza Virus Infection in a Type I Interferon-Dependent Manner.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 18;12:697162. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.697162. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484196 Free PMC article.
-
IL-10 from plasmacytoid dendritic cells promotes angiogenesis in the early stage of endometriosis.J Pathol. 2019 Dec;249(4):485-497. doi: 10.1002/path.5339. Epub 2019 Oct 6. J Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31418859 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin αvβ3 Limits Cytokine Production by Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells and Restricts TLR-Driven Autoimmunity.J Immunol. 2024 Jun 1;212(11):1680-1692. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300290. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38607278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ohlsson M, Jonsson R, Brokstad KA. Subcellular redistribution and surface exposure of the Ro52, Ro60 and La48 autoantigens during apoptosis in human ductal epithelial cells: a possible mechanism in the pathogenesis of Sjogren’s syndrome. Scand J Immunol (2002) 56:456–69.10.1046/j.1365-3083.2002.01072_79.x - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

