Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in the Only Hearing Ear: Large Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome
- PMID: 28018692
- PMCID: PMC5149634
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/8909124
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss in the Only Hearing Ear: Large Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome
Abstract
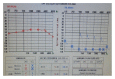
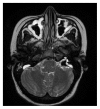
Sudden hearing loss in the only hearing ear cases are rarely published in the English literature; most of the cases are idiopathic. It is an otologic emergency needing urgent treatment. Delayed diagnosis can interfere with patient's social life with interrupting the verbal communication. In this case report we presented a 33-year-old female patient having sudden sensorineural hearing loss in the only hearing ear diagnosed as bilateral large vestibular aqueduct syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Sudden deafness with large vestibular aqueduct (case report and literatures review)].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2002 Oct;16(10):515-7. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Ke Za Zhi. 2002. PMID: 15515555 Chinese.
-
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for sudden sensorineural hearing loss in large vestibular aqueduct syndrome.J Laryngol Otol. 2014 Jan;128 Suppl 1:S50-4. doi: 10.1017/S0022215113001308. Epub 2013 Jun 6. J Laryngol Otol. 2014. PMID: 23739031
-
Vestibular aqueduct in sudden sensorineural hearing loss.J Laryngol Otol. 2008 Sep;122(9):887-92. doi: 10.1017/S0022215107000941. Epub 2007 Nov 26. J Laryngol Otol. 2008. PMID: 18036279
-
Large vestibular aqueduct syndrome and endolymphatic hydrops: two presentations of a common primary inner-ear dysfunction?J Laryngol Otol. 2009 Aug;123(8):919-21. doi: 10.1017/S0022215108004088. Epub 2008 Nov 12. J Laryngol Otol. 2009. PMID: 19000343 Review.
-
The large vestibular aqueduct syndrome in children. A review of 12 cases and the description of a new clinical entity.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1989 Jan;115(1):54-8. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1989.01860250056026. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1989. PMID: 2642380 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effectiveness of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy as Salvage Treatment for Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Retrospective Study.Cureus. 2020 Oct 6;12(10):e10819. doi: 10.7759/cureus.10819. Cureus. 2020. PMID: 33173627 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pyykkö I., Ishizaki H., Peltomaa M. Azathioprine with cortisone in treatment of hearing loss in only hearing ear. Acta Oto-Laryngologica. Supplementum. 1997;529:83–85. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources