Hand Impairment in Systemic Sclerosis: Various Manifestations and Currently Available Treatment
- PMID: 28018840
- PMCID: PMC5176259
- DOI: 10.1007/s40674-016-0052-9
Hand Impairment in Systemic Sclerosis: Various Manifestations and Currently Available Treatment
Abstract
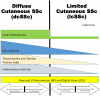
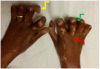
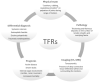
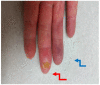
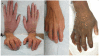
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is an autoimmune disease initially recognized by hand involvement due to characteristic Raynaud's phenomenon (RP), puffy hands, skin thickening, and contractures resembling claw deformities. SSc contributes to hand impairment through inflammatory arthritis, joint contractures, tendon friction rubs (TFRs), RP, digital ulcers (DU), puffy hands, skin sclerosis, acro-osteolysis, and calcinosis. These manifestations, which often co-exist, can contribute to difficulty with occupational activities and activities of daily living (ADL), which can result in impaired quality of life. However, despite this knowledge, most diagnostic and treatment principles in SSc are focused on visceral manifestations due to known associations with morbidity and mortality. Treatment of inflammatory arthritis is symptom based and involves corticosteroids ≤10mg daily, methotrexate, tumor necrosis factor inhibitors, tocilizumab, and abatacept. Small joint contractures are managed by principles of occupational hand therapy and rarely surgical procedures. TFRs may be treated similar to inflammatory arthritis with corticosteroids. All patients with RP and DU should keep digits covered and warm and avoid vasoconstrictive agents. Pharmacologic management of RP begins with use of calcium channel blockers, but additional agents that may be considered are fluoxetine and phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) inhibitors. DU management also involves vasodilators including calcium channel blockers and PDE5 inhibitors; bosentan has also been shown to prevent DU. In patients with severe RP and active DU, intravenous epoprostenol or iloprost can be used and surgical procedures, such as botulinum injections and digital sympathectomies, may be considered. For those with early diffuse cutaneous SSc needing immunosuppression for skin sclerosis, methotrexate or mycophenolate mofetil can be used, but the agent of choice depends on co-existing manifestations, such as inflammatory arthritis and/or lung involvement. Various pharmacologic agents for calcinosis have been considered but are generally ineffective; however, surgical options, including excision of areas of calcinosis, can be considered. Overall management of hand impairment for all patients with SSc should include occupational hand therapy techniques such as range of motion exercises, paraffin wax, and devices to assist in ADL. Thus, treatment options for the various manifestations contributing to hand impairment in SSc are limited and often modestly efficacious at best. Robust studies are needed to address the manifestations of SSc that contribute to hand impairment.
Keywords: Raynaud's phenomenon; acro-osteolysis; arthralgias; calcinosis; digital ulcers; hand impairment; hand involvement; inflammatory arthritis; joint contractures; puffy hands; scleroderma; skin sclerosis; systemic sclerosis; tendon friction rubs.
Figures
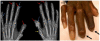

Similar articles
-
Development of a Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Protocol to Evaluate Hand Pain in Systemic Sclerosis Patients.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Mar 22;14(7):669. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14070669. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38611582 Free PMC article.
-
Digital ulcers and cutaneous subsets of systemic sclerosis: Clinical, immunological, nailfold capillaroscopy, and survival differences in the Spanish RESCLE Registry.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016 Oct;46(2):200-208. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 May 18. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016. PMID: 27312381
-
Emerging treatments for scleroderma/systemic sclerosis.Fac Rev. 2021 May 5;10:43. doi: 10.12703/r/10-43. eCollection 2021. Fac Rev. 2021. PMID: 34131653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Treatment Algorithms for Systemic Sclerosis According to Experts.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018 Nov;70(11):1820-1828. doi: 10.1002/art.40560. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29781586
-
Management of Widespread Skin Thickening in Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis.Curr Treatm Opt Rheumatol. 2016 Mar;2(1):49-60. doi: 10.1007/s40674-016-0040-0. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Curr Treatm Opt Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27330933 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ultrasound assessment of skin thickness and stiffness: the correlation with histology and clinical score in systemic sclerosis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2020 Aug 26;22(1):197. doi: 10.1186/s13075-020-02285-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32843083 Free PMC article.
-
Extension-elicited blanching of the dorsal phalanges in systemic sclerosis: A case series.JAAD Case Rep. 2022 Sep 19;30:87-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2022.09.005. eCollection 2022 Dec. JAAD Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36411842 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pain and Self-Efficacy Among Patients With Systemic Sclerosis: A Scleroderma Patient-Centered Intervention Network Cohort Study.Nurs Res. 2021 Set/Oct 01;70(5):334-343. doi: 10.1097/NNR.0000000000000528. Nurs Res. 2021. PMID: 34173376 Free PMC article.
-
Fat Grafting Subjectively Improves Facial Skin Elasticity and Hand Function of Scleroderma Patients.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021 Jan 25;9(1):e3373. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000003373. eCollection 2021 Jan. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2021. PMID: 33552819 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose-Derived Regenerative Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Hand Dysfunction in Systemic Sclerosis: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022 Aug;74(8):1399-1408. doi: 10.1002/art.42133. Epub 2022 Jun 27. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 35358372 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Sandqvist G, Eklund M, Akesson A, Nordenskiold U. Daily activities and hand function in women with scleroderma. Scandinavian journal of rheumatology. 2004;33(2):102–7. - PubMed
-
- Avouac J, Clements PJ, Khanna D, Furst DE, Allanore Y. Articular involvement in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology. 2012;51(8):1347–56. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes041. - PubMed
-
- Avouac J, Walker U, Tyndall A, Kahan A, Matucci-Cerinic M, Allanore Y, et al. Characteristics of joint involvement and relationships with systemic inflammation in systemic sclerosis: results from the EULAR Scleroderma Trial and Research Group (EUSTAR) database. The Journal of rheumatology. 2010;37(7):1488–501. doi:10.3899/jrheum.091165. - PubMed
-
- Avouac J, Walker UA, Hachulla E, Riemekasten G, Cuomo G, Carreira PE, et al. Joint and tendon involvement predict disease progression in systemic sclerosis: a EUSTAR prospective study. Annals of the rheumatic diseases. 2016;75(1):103–9. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205295. - PubMed
-
- Morrisroe KB, Nikpour M, Proudman SM. Musculoskeletal Manifestations of Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatic diseases clinics of North America. 2015;41(3):507–18. doi:10.1016/j.rdc.2015.04.011. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
