Role of BKCa in Stretch-Induced Relaxation of Colonic Smooth Muscle
- PMID: 28018918
- PMCID: PMC5149602
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9497041
Role of BKCa in Stretch-Induced Relaxation of Colonic Smooth Muscle
Abstract
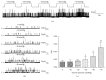
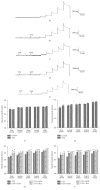
Stretch-induced relaxation has not been clearly identified in gastrointestinal tract. The present study is to explore the role of large conductance calcium-activated potassium channels (BKCa) in stretch-induced relaxation of colon. The expression and currents of BKCa were detected and the basal muscle tone and contraction amplitude of colonic smooth muscle strips were measured. The expression of BKCa in colon is higher than other GI segments (P < 0.05). The density of BKCa currents was very high in colonic smooth muscle cells (SMCs). BKCa in rat colonic SMCs were sensitive to stretch. The relaxation response of colonic SM strips to stretch was attenuated by charybdotoxin (ChTX), a nonspecific BKCa blocker (P < 0.05). After blocking enteric nervous activities by tetrodotoxin (TTX), the stretch-induced relaxation did not change (P > 0.05). Still, ChTX and iberiotoxin (IbTX, a specific BKCa blocker) attenuated the relaxation of the colonic muscle strips enduring stretch (P < 0.05). These results suggest stretch-activation of BKCa in SMCs was involved in the stretch-induced relaxation of colon. Our study highlights the role of mechanosensitive ion channels in SMCs in colon motility regulation and their physiological and pathophysiological significance is worth further study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Relaxant effect of flavonoid naringenin on contractile activity of rat colonic smooth muscle.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Sep 11;155(2):1177-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.06.053. Epub 2014 Jul 2. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24997391
-
Hydrogen sulfide regulates the colonic motility by inhibiting both L-type calcium channels and BKCa channels in smooth muscle cells of rat colon.PLoS One. 2015 Mar 26;10(3):e0121331. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0121331. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25811907 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanism of apelin-13 regulation of colonic motility in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 5;904:174149. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174149. Epub 2021 May 5. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33961873
-
The role of mechanosensitive ion channels in the gastrointestinal tract.Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 19;13:904203. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.904203. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36060694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein kinase C isoenzymes: a review of their structure, regulation and role in regulating airways smooth muscle tone and mitogenesis.Br J Pharmacol. 2000 Aug;130(7):1433-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703452. Br J Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 10928943 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Targeting Lipid-Ion Channel Interactions in Cardiovascular Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 May 6;9:876634. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.876634. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35600482 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen inhibits colonic smooth muscle contractions by regulating BKβ1 signaling.PLoS One. 2023 Nov 10;18(11):e0294249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294249. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37948436 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanotransduction at the Plasma Membrane-Cytoskeleton Interface.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 26;22(21):11566. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111566. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of xenobiotics in triggering psoriasis.Arch Toxicol. 2020 Dec;94(12):3959-3982. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02870-8. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Arch Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32833044 Review.
-
Mechanotransduction in gastrointestinal smooth muscle cells: role of mechanosensitive ion channels.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 May 1;320(5):G897-G906. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00481.2020. Epub 2021 Mar 17. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33729004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lin Y.-M., Fu Y., Wu C. C., Xu G.-Y., Huang L.-Y., Shi X.-Z. Colon distention induces persistent visceral hypersensitivity by mechanotranscription of pain mediators in colonic smooth muscle cells. American Journal of Physiology—Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology. 2015;308(5):G434–G441. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00328.2014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davis M. J., Hill M. A. Signaling mechanisms underlying the vascular myogenic response. Physiological Reviews. 1999;79(2):387–423. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

