Noise performance of low-dose CT: comparison between an energy integrating detector and a photon counting detector using a whole-body research photon counting CT scanner
- PMID: 28018936
- PMCID: PMC5155128
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.3.4.043503
Noise performance of low-dose CT: comparison between an energy integrating detector and a photon counting detector using a whole-body research photon counting CT scanner
Abstract
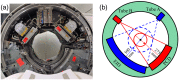
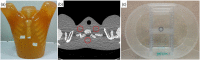
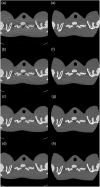
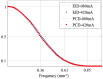
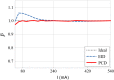
Photon counting detector (PCD)-based computed tomography (CT) is an emerging imaging technique. Compared to conventional energy integrating detector (EID)-based CT, PCD-CT is able to exclude electronic noise that may severely impair image quality at low photon counts. This work focused on comparing the noise performance at low doses between the PCD and EID subsystems of a whole-body research PCD-CT scanner, both qualitatively and quantitatively. An anthropomorphic thorax phantom was scanned, and images of the shoulder portion were reconstructed. The images were visually and quantitatively compared between the two subsystems in terms of streak artifacts, an indicator of the impact of electronic noise. Furthermore, a torso-shaped water phantom was scanned using a range of tube currents. The product of the noise and the square root of the tube current was calculated, normalized, and compared between the EID and PCD subsystems. Visual assessment of the thorax phantom showed that electronic noise had a noticeably stronger degrading impact in the EID images than in the PCD images. The quantitative results indicated that in low-dose situations, electronic noise had a noticeable impact (up to a 5.8% increase in magnitude relative to quantum noise) on the EID images, but negligible impact on the PCD images.
Keywords: computed tomography; electronic noise; low dose; photon counting.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

