Carbamate Insecticides Target Human Melatonin Receptors
- PMID: 28027439
- PMCID: PMC5318275
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.6b00301
Carbamate Insecticides Target Human Melatonin Receptors
Abstract
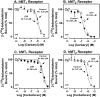
Carbaryl (1-naphthyl methylcarbamate) and carbofuran (2,3-dihydro-2,2-dimethyl-7-benzofuranyl methylcarbamate) are among the most toxic insecticides, implicated in a variety of diseases including diabetes and cancer among others. Using an integrated pharmacoinformatics based screening approach, we have identified these insecticides to be structural mimics of the neurohormone melatonin and were able to bind to the putative melatonin binding sites in MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors in silico. Carbaryl and carbofuran then were tested for competition with 2-[125I]-iodomelatonin (300 pM) binding to hMT1 or hMT2 receptors stably expressed in CHO cells. Carbaryl and carbofuran showed higher affinity for competition with 2-[125I]-iodomelatonin binding to the hMT2 compared to the hMT1 melatonin receptor (33 and 35-fold difference, respectively) as predicted by the molecular modeling. In the presence of GTP (100 μM), which decouples the G-protein linked receptors to modulate signaling, the apparent efficacy of carbaryl and carbofuran for 2-[125I]-iodomelatonin binding for the hMT1 melatonin receptor was not affected but significantly decreased for the hMT2 melatonin receptor compatible with receptor antagonist/inverse agonist and agonist efficacy, respectively. Altogether, our data points to a potentially new mechanism through which carbamate insecticides carbaryl and carbofuran could impact human health by altering the homeostatic balance of key regulatory processes by directly binding to melatonin receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Dubocovich ML. Melatonin receptors: role on sleep and circadian rhythm regulation. Sleep medicine. 2007;8(Suppl 3):34–42. - PubMed
-
- Klein DC. Serotonin N-acetyltransferase. A personal historical perspective. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;460:5–16. - PubMed
-
- Fukuhara C, Dirden JC, Tosini G. Photic regulation of melatonin in rat retina and the role of proteasomal proteolysis. NeuroReport. 2001;12:3833–3837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

