Novel Chemical Scaffolds for Inhibition of Rifamycin-Resistant RNA Polymerase Discovered from High-Throughput Screening
- PMID: 28027449
- PMCID: PMC5323270
- DOI: 10.1177/2472555216679994
Novel Chemical Scaffolds for Inhibition of Rifamycin-Resistant RNA Polymerase Discovered from High-Throughput Screening
Abstract
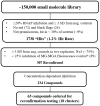
Rifampin has been a cornerstone of tuberculosis (TB) treatment since its introduction. The rise of multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant TB makes the development of novel therapeutics effective against these strains an urgent need. Site-specific mutations in the target enzyme of rifampin, RNA polymerase (RNAP) comprises the majority (~97%) of rifamycin-resistant (RifR) strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB). To identify novel inhibitors of bacterial RNAP, an in vitro plasmid-based transcription assay that uses malachite green (MG) to detect transcribed RNA containing MG aptamers was developed. This assay was optimized in a 384-well plate format and used to screen 150,000 compounds against an Escherichia coli homolog of the most clinically relevant RifR RNAP (βS531L) containing a mutation (β'V408G) that compensates for the fitness defect of this RifR mutant. Following confirmation and concentration-response studies, 10 compounds were identified with similar in vitro inhibition values across a panel of wild-type and RifR E. coli and MTB RNAPs. Four compounds identified from the screen are active against MTB in culture at concentrations below 200 µM. Initial follow-up has resulted in the elimination of one scaffold due to potential pan-assay interference.
Keywords: RNA polymerase; antibiotic resistance; high-throughput screen; rifampin; tuberculosis.
Figures

References
-
- UNAIDS. Fact Sheet 2016. UNAIDS; 2016. http://www.unaids.org/
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2016. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2016.
-
- Mukhtar TA, Wright GD. Streptogramins, oxazolidinones, and other inhibitors of bacterial protein synthesis. Chem Rev. 2005;105(2):529–542. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

