Ohr plays a central role in bacterial responses against fatty acid hydroperoxides and peroxynitrite
- PMID: 28028230
- PMCID: PMC5240686
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1619659114
Ohr plays a central role in bacterial responses against fatty acid hydroperoxides and peroxynitrite
Abstract
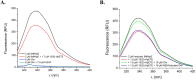
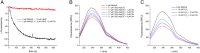
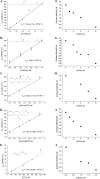
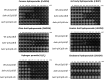
Organic hydroperoxide resistance (Ohr) enzymes are unique Cys-based, lipoyl-dependent peroxidases. Here, we investigated the involvement of Ohr in bacterial responses toward distinct hydroperoxides. In silico results indicated that fatty acid (but not cholesterol) hydroperoxides docked well into the active site of Ohr from Xylella fastidiosa and were efficiently reduced by the recombinant enzyme as assessed by a lipoamide-lipoamide dehydrogenase-coupled assay. Indeed, the rate constants between Ohr and several fatty acid hydroperoxides were in the 107-108 M-1⋅s-1 range as determined by a competition assay developed here. Reduction of peroxynitrite by Ohr was also determined to be in the order of 107 M-1⋅s-1 at pH 7.4 through two independent competition assays. A similar trend was observed when studying the sensitivities of a ∆ohr mutant of Pseudomonas aeruginosa toward different hydroperoxides. Fatty acid hydroperoxides, which are readily solubilized by bacterial surfactants, killed the ∆ohr strain most efficiently. In contrast, both wild-type and mutant strains deficient for peroxiredoxins and glutathione peroxidases were equally sensitive to fatty acid hydroperoxides. Ohr also appeared to play a central role in the peroxynitrite response, because the ∆ohr mutant was more sensitive than wild type to 3-morpholinosydnonimine hydrochloride (SIN-1 , a peroxynitrite generator). In the case of H2O2 insult, cells treated with 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole (a catalase inhibitor) were the most sensitive. Furthermore, fatty acid hydroperoxide and SIN-1 both induced Ohr expression in the wild-type strain. In conclusion, Ohr plays a central role in modulating the levels of fatty acid hydroperoxides and peroxynitrite, both of which are involved in host-pathogen interactions.
Keywords: Cys-based peroxidase; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; hydroperoxides; pathogenic bacteria; thiols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
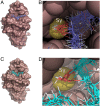


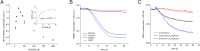

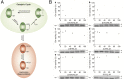
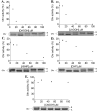



References
-
- Flohé L. The impact of thiol peroxidases on redox regulation. Free Radic Res. 2016;50(2):126–142. - PubMed
-
- Winterbourn CC, Hampton MB. Thiol chemistry and specificity in redox signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008;45(5):549–561. - PubMed
-
- Peskin AV, et al. The high reactivity of peroxiredoxin 2 with H2O2 is not reflected in its reaction with other oxidants and thiol reagents. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(16):11885–11892. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

