Nrf2 mitigates LRRK2- and α-synuclein-induced neurodegeneration by modulating proteostasis
- PMID: 28028237
- PMCID: PMC5293055
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1522872114
Nrf2 mitigates LRRK2- and α-synuclein-induced neurodegeneration by modulating proteostasis
Abstract
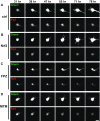
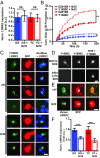
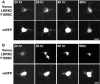
Mutations in leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) and α-synuclein lead to Parkinson's disease (PD). Disruption of protein homeostasis is an emerging theme in PD pathogenesis, making mechanisms to reduce the accumulation of misfolded proteins an attractive therapeutic strategy. We determined if activating nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor (Nrf2), a potential therapeutic target for neurodegeneration, could reduce PD-associated neuron toxicity by modulating the protein homeostasis network. Using a longitudinal imaging platform, we visualized the metabolism and location of mutant LRRK2 and α-synuclein in living neurons at the single-cell level. Nrf2 reduced PD-associated protein toxicity by a cell-autonomous mechanism that was time-dependent. Furthermore, Nrf2 activated distinct mechanisms to handle different misfolded proteins. Nrf2 decreased steady-state levels of α-synuclein in part by increasing α-synuclein degradation. In contrast, Nrf2 sequestered misfolded diffuse LRRK2 into more insoluble and homogeneous inclusion bodies. By identifying the stress response strategies activated by Nrf2, we also highlight endogenous coping responses that might be therapeutically bolstered to treat PD.
Keywords: LRRK2; Nrf2; Parkinson’s disease; proteostasis; α-synuclein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
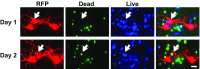

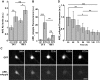
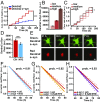
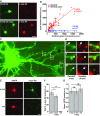
Comment in
-
Combating Parkinson's disease-associated toxicity by modulating proteostasis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Jan 31;114(5):803-804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1620082114. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017. PMID: 28096350 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Polymeropoulos MH, et al. Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science. 1997;276(5321):2045–2047. - PubMed
-
- Paisán-Ruíz C, et al. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson’s disease. Neuron. 2004;44(4):595–600. - PubMed
-
- Clark LN, et al. Frequency of LRRK2 mutations in early- and late-onset Parkinson disease. Neurology. 2006;67(10):1786–1791. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

