Effect of Continuous B Cell Depletion With Rituximab on Pathogenic Autoantibodies and Total IgG Levels in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis
- PMID: 28029751
- PMCID: PMC5543686
- DOI: 10.1002/art.40032
Effect of Continuous B Cell Depletion With Rituximab on Pathogenic Autoantibodies and Total IgG Levels in Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of rituximab on pathogenic autoantibodies and total Ig levels, and to identify serious adverse events in patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) treated with continuous B cell depletion.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective analysis of 239 patients with AAV treated with rituximab-induced continuous B cell depletion. Two treatment cohorts were analyzed: an induction group (n = 52) and a maintenance group (n = 237). Changes in ANCA titers and total Ig levels over time were evaluated using mixed-effects models. Risk factors for serious infections during maintenance treatment were evaluated using Poisson regression.
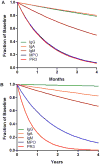
Results: During induction, IgG levels fell at a mean rate of 6% per month (95% confidence interval [95% CI] 4, 8%), while ANCA levels declined at a mean rate of 47% per month (95% CI 42, 52%) and 48% per month (95% CI 42, 54%) for patients with antimyeloperoxidase (anti-MPO) antibodies and those with anti-proteinase 3 (anti-PR3) antibodies, respectively. During maintenance treatment, with a median duration of 2.4 years (interquartile range 1.5, 4.0 years), IgG levels declined a mean of 0.6% per year (95% CI -0.2, 1.4%). New significant hypogammaglobulinemia (IgG level of <400 mg/dl) during maintenance treatment occurred in 4.6% of the patients, all of whom were in the lowest baseline IgG quartile. Serious infections during maintenance therapy occurred at a rate of 0.85 per 10 patient-years (95% CI 0.66, 1.1) and were independently associated with an IgG level of <400 mg/dl.
Conclusion: B cell-targeted therapy causes a preferential decline in ANCA titers relative to total IgG levels. Despite prolonged maintenance therapy with rituximab, IgG levels remain essentially constant. Serious infections were rare.
© 2016, American College of Rheumatology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Reply.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Oct;69(10):2095-2096. doi: 10.1002/art.40210. Epub 2017 Aug 15. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28692761 No abstract available.
-
Rituximab for Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis-Not Everything in the Garden Is Rosy: Comment on the Article by Cortazar et al.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Oct;69(10):2094-2095. doi: 10.1002/art.40209. Epub 2017 Aug 22. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28692783 No abstract available.
References
-
- Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, et al. Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2004 Jun 17;350(25):2572–81. - PubMed
-
- Cambridge G, Leandro MJ, Edwards JC, Ehrenstein MR, Salden M, Bodman-Smith M, et al. Serologic changes following B lymphocyte depletion therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003 Aug;48(8):2146–54. - PubMed
-
- Smith KG, Jones RB, Burns SM, Jayne DR. Long-term comparison of rituximab treatment for refractory systemic lupus erythematosus and vasculitis: Remission, relapse, and re-treatment. Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Sep;54(9):2970–82. - PubMed
-
- Cambridge G, Leandro MJ, Teodorescu M, Manson J, Rahman A, Isenberg DA, et al. B cell depletion therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus: effect on autoantibody and antimicrobial antibody profiles. Arthritis Rheum. 2006 Nov;54(11):3612–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

