Enablers and barriers to implementing collaborative care for anxiety and depression: a systematic qualitative review
- PMID: 28031028
- PMCID: PMC5192575
- DOI: 10.1186/s13012-016-0519-y
Enablers and barriers to implementing collaborative care for anxiety and depression: a systematic qualitative review
Abstract
Background: Collaborative care is an increasingly popular approach for improving quality of care for people with mental health problems through an intensified and structured collaboration between primary care providers and health professionals with specialized psychiatric expertise. Trials have shown significant positive effects for patients suffering from depression, but since collaborative care is a complex intervention, it is important to understand the factors which affect its implementation. We present a qualitative systematic review of the enablers and barriers to implementing collaborative care for patients with anxiety and depression.
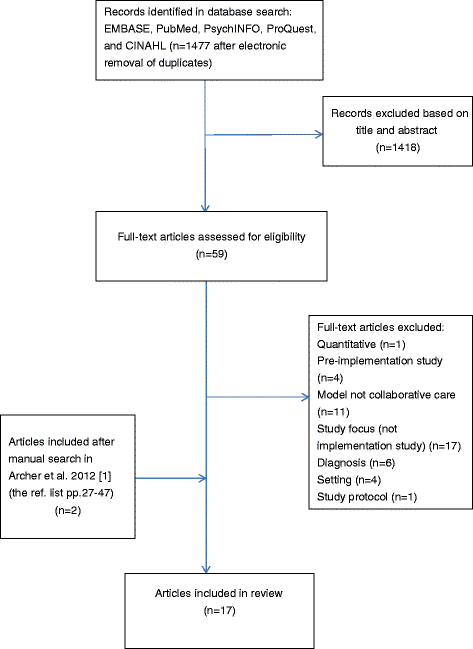
Methods: We developed a comprehensive search strategy in cooperation with a research librarian and performed a search in five databases (EMBASE, PubMed, PsycINFO, ProQuest, and CINAHL). All authors independently screened titles and abstracts and reviewed full-text articles. Studies were included if they were published in English and based on the original qualitative data on the implementation of a collaborative care intervention targeted at depression or anxiety in an adult patient population in a high-income country. Our subsequent analysis employed the normalization process theory (NPT).
Results: We included 17 studies in our review of which 11 were conducted in the USA, five in the UK, and one in Canada. We identified several barriers and enablers within the four major analytical dimensions of NPT. Securing buy-in among primary care providers was found to be critical but sometimes difficult. Enablers included physician champions, reimbursement for extra work, and feedback on the effectiveness of collaborative care. The social and professional skills of the care managers seemed critical for integrating collaborative care in the primary health care clinic. Day-to-day implementation was also found to be facilitated by the care managers being located in the clinic since this supports regular face-to-face interactions between physicians and care managers.
Conclusions: The following areas require special attention when planning collaborative care interventions: effective educational programs, especially for care managers; issues of reimbursement in relation to primary care providers; good systems for communication and monitoring; and promoting face-to-face interaction between care managers and physicians, preferably through co-location. There is a need for well-sampled, in-depth qualitative studies on the implementation of collaborative care in settings outside the USA and the UK.
Keywords: Anxiety; Barriers; Collaborative care; Depression; Enablers; Implementation; Qualitative review; Shared care.
References
-
- Archer J, Bower P, Gilbody S, Lovell K, Richards D, Gask L, et al. Collaborative care for depression and anxiety problems. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;(10):CD006525. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD006525.pub2/full. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical