Dietary biomarker evaluation in a controlled feeding study in women from the Women's Health Initiative cohort
- PMID: 28031191
- PMCID: PMC5267309
- DOI: 10.3945/ajcn.116.144840
Dietary biomarker evaluation in a controlled feeding study in women from the Women's Health Initiative cohort
Abstract
Background: Controlled human feeding studies are necessary for robust nutritional biomarker development and validation. Previous feeding studies have typically evaluated single nutrients and tested relatively few diets.
Objectives: The objectives were 1) to simultaneously associate dietary intake with a range of potential nutritional biomarkers in postmenopausal women by using a controlled feeding study whereby each participant was provided a diet similar to her usual diet and 2) to evaluate serum concentrations of select nutrients as potential biomarkers with the use of established urinary recovery biomarkers of energy and protein as benchmarks for evaluation.
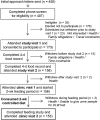
Design: Postmenopausal women from the Women's Health Initiative (n = 153) were provided with a 2-wk controlled diet in which each individual's menu approximated her habitual food intake as estimated from her 4-d food record and adjusted for estimated energy requirements. Serum biomarkers, including carotenoids, tocopherols, folate, vitamin B-12, and phospholipid fatty acids, were collected at the beginning and end of the feeding period. Doubly labeled water and urinary nitrogen biomarkers were used to derive estimates of energy and protein consumption, respectively.
Results: Linear regression of (ln-transformed) consumed nutrients on (ln-transformed) potential biomarkers and participant characteristics led to the following regression (R2) values for serum concentration biomarkers: folate, 0.49; vitamin B-12, 0.51; α-carotene, 0.53; β-carotene, 0.39; lutein + zeaxanthin, 0.46; lycopene, 0.32; and α-tocopherol, 0.47. R2 values for percentage of energy from polyunsaturated fatty acids and urinary recovery biomarkers of energy and protein intakes were 0.27, 0.53, and 0.43, respectively. Phospholipid saturated fatty acids and monounsaturated fatty acids and serum γ-tocopherol were weakly associated with intake (R2 < 0.25).
Conclusions: Serum concentration biomarkers of several vitamins and carotenoids performed similarly to established energy and protein urinary recovery biomarkers in representing nutrient intake variation in a feeding study, and thus are likely suitable for application in this population of postmenopausal women. Further work is needed to identify objective measures of categories of fatty acid intake. This trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov as NCT00000611.
Keywords: carotenoids; doubly labeled water; energy; fatty acids; folate; human feeding study; nutrition assessment; protein; tocopherols; vitamin B-12.
© 2017 American Society for Nutrition.
Figures
Comment in
-
The nutritional metabolomics crossroads: how to ensure success for dietary biomarkers.Am J Clin Nutr. 2017 Feb;105(2):293-294. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.116.150847. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017. PMID: 28100510 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Zheng C, Beresford SA, Van Horn L, Tinker LF, Thomson CA, Neuhouser ML, Di C, Manson JE, Mossavar-Rahmani Y, Seguin R, et al. Simultaneous association of total energy consumption and activity-related energy expenditure with risks of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and diabetes among postmenopausal women. Am J Epidemiol 2014;180:526–35. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Knowler WC, Fowler SE, Hamman RF, Christophi CA, Hoffman HJ, Brenneman AT, Brown-Friday JO, Goldberg R, Venditti E, et al. ; Diabetes Prevention Program Research Group. 10-Year follow-up of diabetes incidence and weight loss in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study. Lancet 2009;374:1677–86. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Eckel RH, Jakicic JM, Ard JD, de Jesus JM, Houston Miller N, Hubbard VS, Lee IM, Lichtenstein AH, Loria CM, Millen BE, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC guideline on lifestyle management to reduce cardiovascular risk: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;63:2960–84. - PubMed
-
- Catsburg C, Miller AB, Rohan TE. Adherence to cancer prevention guidelines and risk of breast cancer. Int J Cancer 2014;135:2444–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical