Emergence of Ceftazidime-Avibactam Resistance Due to Plasmid-Borne blaKPC-3 Mutations during Treatment of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections
- PMID: 28031201
- PMCID: PMC5328542
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02097-16
Emergence of Ceftazidime-Avibactam Resistance Due to Plasmid-Borne blaKPC-3 Mutations during Treatment of Carbapenem-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Infections
Abstract
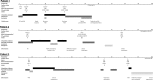
Ceftazidime-avibactam is a novel β-lactam/β-lactamase inhibitor with activity against carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) that produce Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC). We report the first cases of ceftazidime-avibactam resistance to develop during treatment of CRE infections and identify resistance mechanisms. Ceftazidime-avibactam-resistant K. pneumoniae emerged in three patients after ceftazidime-avibactam treatment for 10 to 19 days. Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) of longitudinal ceftazidime-avibactam-susceptible and -resistant K. pneumoniae isolates was used to identify potential resistance mechanisms. WGS identified mutations in plasmid-borne blaKPC-3, which were not present in baseline isolates. blaKPC-3 mutations emerged independently in isolates of a novel sequence type 258 sublineage and resulted in variant KPC-3 enzymes. The mutations were validated as resistance determinants by measuring MICs of ceftazidime-avibactam and other agents following targeted gene disruption in K. pneumoniae, plasmid transfer, and blaKPC cloning into competent Escherichia coli In rank order, the impact of KPC-3 variants on ceftazidime-avibactam MICs was as follows: D179Y/T243M double substitution > D179Y > V240G. Remarkably, mutations reduced meropenem MICs ≥4-fold from baseline, restoring susceptibility in K. pneumoniae from two patients. Cefepime and ceftriaxone MICs were also reduced ≥4-fold against D179Y/T243M and D179Y variant isolates, but susceptibility was not restored. Reverse transcription-PCR revealed that expression of blaKPC-3 encoding D179Y/T243M and D179Y variants was diminished compared to blaKPC-3 expression in baseline isolates. In conclusion, the development of resistance-conferring blaKPC-3 mutations in K. pneumoniae within 10 to 19 days of ceftazidime-avibactam exposure is troubling, but clinical impact may be ameliorated if carbapenem susceptibility is restored in certain isolates.
Keywords: Klebsiella pneumoniae; Klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase; carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae; ceftazidime-avibactam; resistance; sequence type 258.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

References
-
- Tumbarello M, Trecarichi EM, De Rosa FG, Giannella M, Giacobbe DR, Bassetti M, Losito AR, Bartoletti M, Del Bono V, Corcione S, Maiuro G, Tedeschi S, Celani L, Cardellino CS, Spanu T, Marchese A, Ambretti S, Cauda R, Viscoli C, Viale P, Isgri S. 2015. Infections caused by KPC-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae: differences in therapy and mortality in a multicentre study. J Antimicrob Chemother 70:2133–2143. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkv086. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Daikos GL, Tsaousi S, Tzouvelekis LS, Anyfantis I, Psichogiou M, Argyropoulou A, Stefanou I, Sypsa V, Miriagou V, Nepka M, Georgiadou S, Markogiannakis A, Goukos D, Skoutelis A. 2014. Carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae bloodstream infections: lowering mortality by antibiotic combination schemes and the role of carbapenems. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 58:2322–2328. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02166-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

