Implementation of Rapid Molecular Infectious Disease Diagnostics: the Role of Diagnostic and Antimicrobial Stewardship
- PMID: 28031432
- PMCID: PMC5328439
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02264-16
Implementation of Rapid Molecular Infectious Disease Diagnostics: the Role of Diagnostic and Antimicrobial Stewardship
Abstract
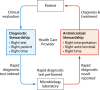
New rapid molecular diagnostic technologies for infectious diseases enable expedited accurate microbiological diagnoses. However, diagnostic stewardship and antimicrobial stewardship are necessary to ensure that these technologies conserve, rather than consume, additional health care resources and optimally affect patient care. Diagnostic stewardship is needed to implement appropriate tests for the clinical setting and to direct testing toward appropriate patients. Antimicrobial stewardship is needed to ensure prompt appropriate clinical action to translate faster diagnostic test results in the laboratory into improved outcomes at the bedside. This minireview outlines the roles of diagnostic stewardship and antimicrobial stewardship in the implementation of rapid molecular infectious disease diagnostics.
Keywords: antimicrobial stewardship; appropriate use criteria; diagnostic stewardship; implementation; rapid diagnostics; utilization.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Integrated Stewardship Model Comprising Antimicrobial, Infection Prevention, and Diagnostic Stewardship (AID Stewardship).J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Nov;55(11):3306-3307. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01283-17. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29066567 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to "Integrated Stewardship Model Comprising Antimicrobial, Infection Prevention, and Diagnostic Stewardship (AID Stewardship)".J Clin Microbiol. 2017 Nov;55(11):3308. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01348-17. J Clin Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29066568 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bartlett RC. 1974. Medical microbiology: quality cost and clinical relevance. Wiley, New York, NY.
-
- Baron EJ, Miller JM, Weinstein MP, Richter SS, Gilligan PH, Thomson RB Jr, Bourbeau P, Carroll KC, Kehl SC, Dunne WM, Robinson-Dunn B, Schwartzman JD, Chapin KC, Snyder JW, Forbes BA, Patel R, Rosenblatt JE, Pritt BS. 2013. A guide to utilization of the microbiology laboratory for diagnosis of infectious diseases: 2013 recommendations by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and the American Society for Microbiology (ASM). Clin Infect Dis 57:e22–e121. doi: 10.1093/cid/cit278. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Poritz MA, Blaschke AJ, Byington CL, Meyers L, Nilsson K, Jones DE, Thatcher SA, Robbins T, Lingenfelter B, Amiott E, Herbener A, Daly J, Dobrowolski SF, Teng DH, Ririe KM. 2011. FilmArray, an automated nested multiplex PCR system for multi-pathogen detection: development and application to respiratory tract infection. PLoS One 6:e26047. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026047. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Blaschke AJ, Heyrend C, Byington CL, Fisher MA, Barker E, Garrone NF, Thatcher SA, Pavia AT, Barney T, Alger GD, Daly JA, Ririe KM, Ota I, Poritz MA. 2012. Rapid identification of pathogens from positive blood cultures by multiplex polymerase chain reaction using the FilmArray system. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 74:349–355. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2012.08.013. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical