CD74 is a novel transcription regulator
- PMID: 28031488
- PMCID: PMC5255621
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1612195114
CD74 is a novel transcription regulator
Abstract
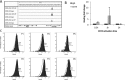
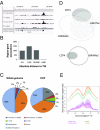
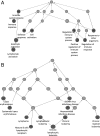
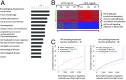
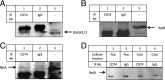
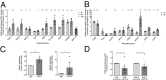
CD74 is a cell-surface receptor for the cytokine macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor binding to CD74 induces its intramembrane cleavage and the release of its cytosolic intracellular domain (CD74-ICD), which regulates cell survival. In the present study, we characterized the transcriptional activity of CD74-ICD in chronic lymphocytic B cells. We show that following CD74 activation, CD74-ICD interacts with the transcription factors RUNX (Runt related transcription factor) and NF-κB and binds to proximal and distal regulatory sites enriched for genes involved in apoptosis, immune response, and cell migration. This process leads to regulation of expression of these genes. Our results suggest that identifying targets of CD74 will help in understanding of essential pathways regulating B-cell survival in health and disease.
Keywords: CD74; CLL; NF-κB; RUNX; transcription.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Stumptner-Cuvelette P, Benaroch P. Multiple roles of the invariant chain in MHC class II function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2002;1542(1-3):1–13. - PubMed
-
- Bucala R, Shachar I. The integral role of CD74 in antigen presentation, MIF signal transduction, and B cell survival and homeostasis. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2014;14(14):1132–1138. - PubMed
-
- Cohen S, Shachar I. Cytokines as regulators of proliferation and survival of healthy and malignant peripheral B cells. Cytokine. 2012;60(1):13–22. - PubMed
-
- Matza D, Kerem A, Medvedovsky H, Lantner F, Shachar I. Invariant chain-induced B cell differentiation requires intramembrane proteolytic release of the cytosolic domain. Immunity. 2002;17(5):549–560. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

