Cell-free methylation markers with diagnostic and prognostic potential in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 28031532
- PMCID: PMC5351641
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14115
Cell-free methylation markers with diagnostic and prognostic potential in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a highly malignant tumor with poor prognosis and high mortality. There is a dearth of effective early diagnostic tools, so liver resection surgery and liver transplantation are the only effective medical treatments. The most commonly used marker for HCC detection is serum alpha fetoprotein (AFP), which has low sensitivity and specificity. Because aberrant DNA methylation of genes and miRNAs occurs early in most cancers, we explored whether circulating methylation markers could be promising clinical tools for HCC diagnosis. Using a whole-genome approach, we identified many hyper-methylated miRNAs in HCC. Furthermore, three abnormally methylated genes and one miRNA were combined to establish a methylation predictive model and tested for its diagnostic and prognostic potential in HCC. Using plasma samples, the predictive model exhibited high sensitivity and specificity (> 80%) for HBV-related HCC. Most importantly, nearly 75% of patients who could not be diagnosed with AFP at 20 ng/mL were detected by this model. Further, the predictive model exhibited an exceedingly high ability to predict 5-year overall survival in HCC patients. These data demonstrate the high diagnostic and prognostic potential of methylation markers in the plasma of HCC patients.
Keywords: DNA methylation; diagnosis; hepatocellular carcinoma; marker; microRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose that they have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
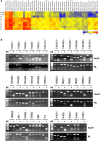

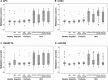
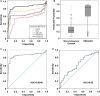

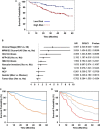
References
-
- Zamcheck N, Pusztaszeri G. CEA. AFP and other potential tumor markers. CA Cancer J Clin. 1975;25:204–214. - PubMed
-
- Millington GW. Genomic imprinting and dermatological disease. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2006;31:681–688. - PubMed
-
- Strathdee G, Brown R. Aberrant DNA methylation in cancer: potential clinical interventions. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2002;4:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Kunej T, Godnic I, Ferdin J, Horvat S, Dovc P, Calin GA. Epigenetic regulation of microRNAs in cancer: an integrated review of literature. Mutat Res. 2011;717:77–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

