Surgical Technique of Total Knee Arthroplasty without Soft Tissue Balance
- PMID: 28032705
- PMCID: PMC6584677
- DOI: 10.1111/os.12289
Surgical Technique of Total Knee Arthroplasty without Soft Tissue Balance
Abstract
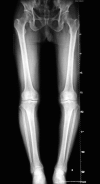
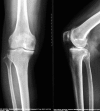
Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) without soft tissue balance can create a balanced knee to a mechanical axis of near neutral with bone cuts, and remove osteophytes thoroughly. In this study, the authors present detailed steps for performing TKA. The attached video demonstrates the TKA procedure. The patient is a 77-year-old man who had suffered from knee pain for 12 years. Physical examination showed the Apley test to be positive and that the range of motion (ROM) decreased. An X-ray filmed at the positive lateral of the knee joint and the double lower extremity revealed a progression of degenerative osteoarthritis with genu varum. The key point of no soft tissue release is to make a rectangular extensional space by osteotomy. In addition, the osteophytes, especially syndesmophytes, should be removed thoroughly. As a result, the ligaments can achieve ideal length and the flexion contracture can also be remedied. Moreover, in surgeries without soft tissue release, bone mass and normal tissue are retained. Patients are satisfied to the surgery not only with less blood loss, anterior knee pain and DVT, but also faster rehabilitation. In summary, TKA without soft tissue balance is an efficient procedure for patients with knee osteoarthritis which can result in good prognosis.
Keywords: Osteophytes; Rectangular osteotomy; Soft tissue balance; Total knee arthroplasty.
© 2016 Chinese Orthopaedic Association and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Prime MS, Palmer J, Khan WS. The national joint registry of England and Wales. Orthopedics, 2011, 34: 107–110. - PubMed
-
- Koh IJ, Kwak DS, Kim TK, Park IJ, In Y. How effective is multiple needle puncturing for medial soft tissue balancing during total knee arthroplasty? A cadaveric study. J Arthroplasty, 2014, 29: 2478–2483. - PubMed
-
- Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS, Elkus M, Rasquinha VJ, Rossi R, Babhulkar S. Total knee arthroplasty for severe valgus deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am, 2005, 86: 2671–2676. - PubMed
-
- Freeman MA, Todd RC, Bamert P, Day WH. ICLH arthroplasty of the knee: 1968‐‐1977. J Bone Joint Surg Br, 1978, 60: 339–344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials