Comparative Effects of Direct Renin Inhibitor and Angiotensin Receptor Blocker on Albuminuria in Hypertensive Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 28033332
- PMCID: PMC5198982
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164936
Comparative Effects of Direct Renin Inhibitor and Angiotensin Receptor Blocker on Albuminuria in Hypertensive Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background: In patients with diabetes, albuminuria is a risk marker of end-stage renal disease and cardiovascular events. An increased renin-angiotensin system activity has been reported to play an important role in the pathological processes in these conditions. We compared the effect of aliskiren, a direct renin inhibitor (DRI), with that of angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) on albuminuria and urinary excretion of angiotensinogen, a marker of intrarenal renin-angiotensin system activity.
Methods: We randomly assigned 237 type 2 diabetic patients with high-normal albuminuria (10 to <30 mg/g of albumin-to-creatinine ratio) or microalbuminuria (30 to <300 mg/g) to the DRI group or ARB group (any ARB) with a target blood pressure of <130/80 mmHg. The primary endpoint was a reduction in albuminuria.
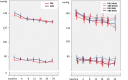
Results: Twelve patients dropped out during the observation period, and a total of 225 patients were analyzed. During the study period, the systolic and diastolic blood pressures were not different between the groups. The changes in the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio from baseline to the end of the treatment period in the DRI and ARB groups were similar (-5.5% and -6.7%, respectively). In contrast, a significant reduction in the urinary excretion of angiotensinogen was observed in the ARB group but not in the DRI group. In the subgroup analysis, a significant reduction in the albuminuria was observed in the ARB group but not in the DRI group among high-normal albuminuria patients.
Conclusion: DRI and ARB reduced albuminuria in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes. In addition, ARB, but not DRI, reduced albuminuria even in patients with normal albuminuria. DRI is not superior to ARB in the reduction of urinary excretion of albumin and angiotensinogen.
Conflict of interest statement
TU has received lecture fee from Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd and research grants from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Astellas Pharma Inc., MSD K.K, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd, Daiichi Sankyo Company Limited and Shionogi & Co., Ltd. HM has received lecture fees from Astellas Pharma Inc., MSD K.K., Daiichi Sankyo Company Limited, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited and research grants from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Astellas Pharma Inc., MSD K.K, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd, Daiichi Sankyo Company Limited and Shionogi & Co., Ltd. MH has received lecture fees from Astellas Pharma Inc., MSD K.K., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Taisho-Toyama Pharm. Co. Ltd, Ono Pharmaceutical, Co., Ltd., Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and research grants from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Astellas Pharma Inc., MSD K.K, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd, Daiichi Sankyo Company Limited and Shionogi & Co., Ltd., and research grants from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Astellas Pharma Inc., MSD K.K, Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd, Daiichi Sankyo Company Limited and Shionogi & Co., Ltd. Taisho-Toyama Pharm. Co. Ltd, Ono Pharmaceutical, Co., Ltd., Bayer Yakuhin Ltd., Pfizer Japan Inc., Eli Lilly Japan K.K., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd. DK has received lecture fees from Astellas Pharma Inc., MSD K.K., Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim Co., Ltd., Astellas Pharma Inc., and Eli Lilly Japan K.K, and research grants from Astellas Pharma Inc., Daiichi Sankyo Company Limited Ono Pharmaceutical, Co., Ltd., Novo Nordisk Pharma Ltd., Sanofi K.K., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Shionogi & Co., Ltd., Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation, Morinaga & Co., Ltd. AN has received lecture fees from Mochida Pharm. Co. Ltd., Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd., Taisho-Toyama Pharm. Co. Ltd., Boehringer-Ingelheim Co., Ltd. and a research grants from Daiichi-Sankyo Co. Ltd., Novartis Co. Ltd., Taisho-Toyama Pharm. Co. Ltd., Chu-gai Pharm. Co., Ltd., Ajinomoto Pharm. Co., Ltd., Mochida Pharma Co., Ltd.. Our competing interest does not alter our adherence to PLOS ONE policies on sharing data ad materials.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

