Combination of nitric oxide and drug delivery systems: tools for overcoming drug resistance in chemotherapy
- PMID: 28034787
- PMCID: PMC5484762
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.12.026
Combination of nitric oxide and drug delivery systems: tools for overcoming drug resistance in chemotherapy
Abstract
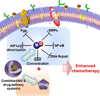
Chemotherapeutic drugs have made significant contributions to anticancer therapy, along with other therapeutic methods including surgery and radiotherapy over the past century. However, multidrug resistance (MDR) of cancer cells has remained as a significant obstacle in the achievement of efficient chemotherapy. Recently, there has been increasing evidence for the potential function of nitric oxide (NO) to overcome MDR. NO is an endogenous and biocompatible molecule, contrasting with other potentially toxic chemosensitizing agents that reverse MDR effects, which has raised expectations in the development of efficient therapeutics with low side effects. In particular, nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems not only facilitate the delivery of multiple therapeutic agents, but also help bypass MDR pathways, which are conducive for the efficient delivery of NO and anticancer drugs, simultaneously. Therefore, this review will discuss the mechanism of NO in overcoming MDR and recent progress of combined NO and drug delivery systems.
Keywords: Cancer; Chemosensitization; Multidrug resistance (MDR); Nanoparticle; Nitric oxide (NO) donor.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures



References
-
- Shapira A, Livney YD, Broxterman HJ, Assaraf YG. Nanomedicine for targeted cancer therapy: Towards the overcoming of drug resistance. Drug Resist. Updates. 2011;14:150–163. - PubMed
-
- Dawar S, Singh N, Kanwar RK, Kennedy RL, Veedu RN, Zhou S-F, Krishnakumar S, Hazra S, Sasidharan S, Duan W, Kanwar JR. Multifunctional and nultitargeted nanoparticles for drug delivery to overcome barriers of drug resistance in human cancers. Drug Discov. Today. 2013;18:1292–1300. - PubMed
-
- HuiHui B, Yu G, YaPing L. Overcoming multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer by nanotechnology. Sci. China Chem. 2010;53:2226–2232.
-
- Shen J, He Q, Gao Y, Shi J, Li Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles loading doxorubicin reverse multidrug resistance: performance and mechanism. Nanoscale. 2011;3:4314–4322. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

