Metoprolol Dose Equivalence in Adult Men and Women Based on Gender Differences: Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulations
- PMID: 28035289
- PMCID: PMC5189989
- DOI: 10.3390/medsci4040018
Metoprolol Dose Equivalence in Adult Men and Women Based on Gender Differences: Pharmacokinetic Modeling and Simulations
Abstract
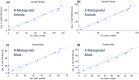
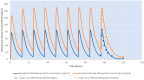
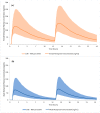
Recent meta-analyses and publications over the past 15 years have provided evidence showing there are considerable gender differences in the pharmacokinetics of metoprolol. Throughout this time, there have not been any research articles proposing a gender stratified dose-adjustment resulting in an equivalent total drug exposure. Metoprolol pharmacokinetic data was obtained from a previous publication. Data was modeled using nonlinear mixed effect modeling using the MONOLIX software package to quantify metoprolol concentration-time data. Gender-stratified dosing simulations were conducted to identify equivalent total drug exposure based on a 100 mg dose in adults. Based on the pharmacokinetic modeling and simulations, a 50 mg dose in adult women provides an approximately similar metoprolol drug exposure to a 100 mg dose in adult men.
Keywords: gender differences; metoprolol; modeling; monolix; pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kotecha D., Manzano L., Krum H., Rosano G., Holmes J., Altman D.G., Collins P.D., Packer M., Wikstrand J., Coats A.J.S., et al. Effect of age and sex on efficacy and tolerability of β blockers in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: Individual patient data meta-analysis. BMJ. 2016;353:i1855. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i1855. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Whitley H.P., Lindsey W. Sex-based differences in drug activity. Am. Fam. Physician. 2009;80:1254–1258. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

