Novel Peptide with Specific Calcium-Binding Capacity from Schizochytrium sp. Protein Hydrolysates and Calcium Bioavailability in Caco-2 Cells
- PMID: 28036002
- PMCID: PMC5295223
- DOI: 10.3390/md15010003
Novel Peptide with Specific Calcium-Binding Capacity from Schizochytrium sp. Protein Hydrolysates and Calcium Bioavailability in Caco-2 Cells
Abstract
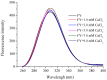
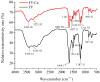
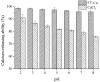
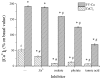
Peptide-calcium can probably be a suitable supplement to improve calcium absorption in the human body. In this study, a specific peptide Phe-Tyr (FY) with calcium-binding capacity was purified from Schizochytrium sp. protein hydrolysates through gel filtration chromatography and reversed phase HPLC. The calcium-binding capacity of FY reached 128.77 ± 2.57 μg/mg. Results of ultraviolet spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, and infrared spectroscopy showed that carboxyl groups, amino groups, and amido groups were the major chelating sites. FY-Ca exhibited excellent thermal stability and solubility, which were beneficial to be absorbed and transported in the basic intestinal tract of the human body. Moreover, the calcium bioavailability in Caco-2 cells showed that FY-Ca could enhance calcium uptake efficiency by more than three times when compared with CaCl₂, and protect calcium ions against dietary inhibitors, such as tannic acid, oxalate, phytate, and Zn2+. Our findings further the progress of algae-based peptide-calcium, suggesting that FY-Ca has the potential to be developed as functionally nutraceutical additives.
Keywords: Schizochytrium sp.; bioavailability; calcium-binding peptide; protein hydrolysate; structure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ngo D.H., Wijesekara I., Vo T.S., Van Ta Q., Kim S.K. Marine food-derived functional ingredients as potential antioxidants in the food industry: An overview. Food Res. Int. 2011;44:523–529. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2010.12.030. - DOI
-
- Yaguchi T., Tanaka S., Yokochi T., Nakahara T., Higashihara T. Production of high yields of docosahexaenoic acid by Schizochytrium sp. strain SR21. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1997;74:1431–1434. doi: 10.1007/s11746-997-0249-z. - DOI
-
- Opheim M., Šližytė R., Sterten H., Provan F., Larssen E., Kjos N.P. Hydrolysis of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) rest raw materials—Effect of raw material and processing on composition, nutritional value, and potential bioactive peptides in the hydrolysates. Process Biochem. 2015;50:1247–1257. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2015.04.017. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

