Dengue Virus-Specific Antibodies Enhance Brazilian Zika Virus Infection
- PMID: 28039355
- PMCID: PMC5854042
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiw638
Dengue Virus-Specific Antibodies Enhance Brazilian Zika Virus Infection
Abstract
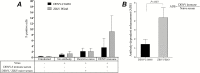
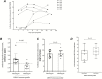
Anti-Flavivirus antibodies are highly cross-reactive and may facilitate Zika virus (ZIKV) infection through the antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) mechanism. We demonstrate that dengue-specific antibodies enhance the infection of a primary Brazilian ZIKV isolate in a FcγRII-expressing K562 cell line. In addition, we demonstrate that serum samples from dengue-immune pregnant women enhanced ZIKV infection. These findings highlight the need for epidemiological studies and animal models to further confirm the role of ADE in the development of congenital and neurological complications associated with ZIKV infections.
Keywords: Zika virus; antibody dependent enhancement; dengue antibodies.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Enhancement of Zika Infection by Dengue Virus-Specific Antibody Is Associated With Low Levels of Antiviral Factors.J Infect Dis. 2017 Sep 1;216(5):612-614. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix344. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28931226 No abstract available.
-
Enhancement of Zika Infection by Dengue-Specific Antibodies Does Not Alter the Production of Interleukin 6 in FcγRII-Expressing K562 Cells.J Infect Dis. 2017 Sep 1;216(5):614-615. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix346. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28931227 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

