REST represses miR-124 and miR-203 to regulate distinct oncogenic properties of glioblastoma stem cells
- PMID: 28040710
- PMCID: PMC5781317
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/now232
REST represses miR-124 and miR-203 to regulate distinct oncogenic properties of glioblastoma stem cells
Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma (GBM) is one of the most common, aggressive, and invasive human brain tumors. There are few reliable mechanism-based therapeutic approaches for GBM patients. The transcriptional repressor RE1 silencing transcriptional factor (REST) regulates the oncogenic properties of a class of GBM stem-like cells (high-REST [HR]-GSCs) in humans. However, it has been unclear whether REST represses specific targets to regulate specific oncogenic functions or represses all targets with overlapping functions in GSCs.
Methods: We used genome-wide, biochemical, and mouse intracranial tumorigenic assays to identify and determine functions of microRNA (miR) targets of REST in 2 independent HR-GSC lines.
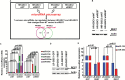
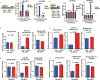
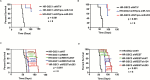
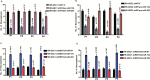
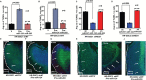
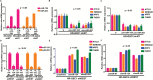
Results: Here we show that REST represses 2 major miR gene targets in HR-GSCs: miR-203, a new target, and miR-124, a known target. Gain of function of miR-124 or miR-203 in HR-GSCs increased survival in tumor-bearing mice. Importantly, the increased survival of tumor-bearing mice caused by knockdown of REST in HR-GSCs was reversed by double knockdown of REST and either miR-203 or miR-124, indicating that these 2 miRs are critical tumor suppressors that are repressed in REST-mediated tumorigenesis. We further show that while miR-124 and the REST-miR-124 pathways regulate self-renewal, apoptosis and invasion, miR-203 and the REST-miR-203 pathways regulate only invasion. We further identify and validate potential mRNA targets of miR-203 and miR-124 in REST-mediated HR-GSC tumor invasion.
Conclusions: These findings indicate that REST regulates its miR gene targets with overlapping functions and suggest how REST maintains oncogenic competence in GSCs. These mechanisms could potentially be utilized to block REST-mediated GBM tumorigenesis.
Keywords: GSCs; REST; apoptosis; invasion; miR-124; miR-203; survival.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Neuro-Oncology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures
Similar articles
-
REST-DRD2 mechanism impacts glioblastoma stem cell-mediated tumorigenesis.Neuro Oncol. 2019 Jun 10;21(6):775-785. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noz030. Neuro Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30953587 Free PMC article.
-
REST regulates oncogenic properties of glioblastoma stem cells.Stem Cells. 2012 Mar;30(3):405-14. doi: 10.1002/stem.1020. Stem Cells. 2012. PMID: 22228704 Free PMC article.
-
Mir-370-3p Impairs Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cell Malignancy Regulating a Complex Interplay between HMGA2/HIF1A and the Oncogenic Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) NEAT1.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 20;21(10):3610. doi: 10.3390/ijms21103610. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32443824 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of cell adhesion molecules in glioblastoma identified prostaglandin F2 receptor inhibitor (PTGFRN) as an essential gene.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jun 11;22(1):642. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09682-2. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35690717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of tumor-suppressive microRNA-218 in targeting glioblastoma stemness.Cancer Lett. 2014 Oct 10;353(1):25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2014.07.011. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 25042866 Review.
Cited by
-
REST-DRD2 mechanism impacts glioblastoma stem cell-mediated tumorigenesis.Neuro Oncol. 2019 Jun 10;21(6):775-785. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noz030. Neuro Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30953587 Free PMC article.
-
miR-124: A Promising Therapeutic Target for Central Nervous System Injuries and Diseases.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Oct;42(7):2031-2053. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01091-6. Epub 2021 Apr 22. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 33886036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
REST upregulates gremlin to modulate diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma vasculature.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 28;9(4):5233-5250. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23750. eCollection 2018 Jan 12. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29435175 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Suppressive Effects of miR-124 and Its Function in Neuronal Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 31;22(11):5919. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115919. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34072894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nerve injury inhibits Oprd1 and Cnr1 transcription through REST in primary sensory neurons.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 4;14(1):26612. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74487-1. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39496614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldape K, Zadeh G, Mansouri S, et al. Glioblastoma: pathology, molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol. 2015; 129(6):829–848. - PubMed
-
- Cloughesy TF, Cavenee WK, Mischel PS. Glioblastoma: from molecular pathology to targeted treatment. Annu Rev Pathol. 2014; 9:1–25. - PubMed
-
- Wick W, Weller M, van den Bent M, et al. MGMT testing—the challenges for biomarker-based glioma treatment. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014; 10(7):372–385. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

