Induction of Expansion and Folding in Human Cerebral Organoids
- PMID: 28041895
- PMCID: PMC6461394
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.11.017
Induction of Expansion and Folding in Human Cerebral Organoids
Abstract
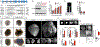
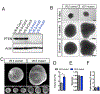
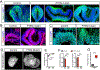
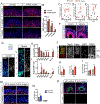
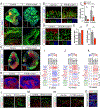
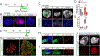
An expansion of the cerebral neocortex is thought to be the foundation for the unique intellectual abilities of humans. It has been suggested that an increase in the proliferative potential of neural progenitors (NPs) underlies the expansion of the cortex and its convoluted appearance. Here we show that increasing NP proliferation induces expansion and folding in an in vitro model of human corticogenesis. Deletion of PTEN stimulates proliferation and generates significantly larger and substantially folded cerebral organoids. This genetic modification allows sustained cell cycle re-entry, expansion of the progenitor population, and delayed neuronal differentiation, all key features of the developing human cortex. In contrast, Pten deletion in mouse organoids does not lead to folding. Finally, we utilized the expanded cerebral organoids to show that infection with Zika virus impairs cortical growth and folding. Our study provides new insights into the mechanisms regulating the structure and organization of the human cortex.
Keywords: AKT; Dengue; PTEN; Zika; cerebral organoids; cortical development; human embryonic stem cells; microcephaly; outer SVZ; outer radial glia.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Of Mice and Men: Species-Specific Organoid Models of Neocortical Malformation.Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Apr 6;20(4):421-422. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.03.005. Cell Stem Cell. 2017. PMID: 28388422
-
You Have Brains in Your Head, You Have Organoids in Your Dish, You Can Steer Yourself in any Direction You Wish.Epilepsy Curr. 2017 Sep-Oct;17(5):311-313. doi: 10.5698/1535-7597.17.5.311. Epilepsy Curr. 2017. PMID: 29225549 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Boland E, Clayton-Smith J, Woo VG, McKee S, Manson FD, Medne L, Zackai E, Swanson EA, Fitzpatrick D, Millen KJ, et al. (2007). Mapping of deletion and translocation breakpoints in 1q44 implicates the serine/threonine kinase AKT3 in postnatal microcephaly and agenesis of the corpus callosum. American journal of human genetics 81, 292–303. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Butler MG, Dasouki MJ, Zhou XP, Talebizadeh Z, Brown M, Takahashi TN, Miles JH, Wang CH, Stratton R, Pilarski R, et al. (2005). Subset of individuals with autism spectrum disorders and extreme macrocephaly associated with germline PTEN tumour suppressor gene mutations. Journal of medical genetics 42, 318–321. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bystron I, Blakemore C, and Rakic P (2008). Development of the human cerebral cortex: Boulder Committee revisited. Nature reviews Neuroscience 9, 110–122. - PubMed
-
- Chenn A, and Walsh CA (2002). Regulation of cerebral cortical size by control of cell cycle exit in neural precursors. Science 297, 365–369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

