Comparing the effects of manual and ultrasonic instrumentation on root surface mechanical properties
- PMID: 28042268
- PMCID: PMC5166309
- DOI: 10.4103/1305-7456.195162
Comparing the effects of manual and ultrasonic instrumentation on root surface mechanical properties
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the current study is to analyze the surface profiles of healthy and periodontal-treated roots. In addition, manual and ultrasonic instrumentation methods have been compared in terms of surface mechanical properties of root surfaces including surface roughness, hardness, and elastic modulus.
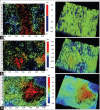
Materials and methods: This study was conducted using extracted teeth that were randomly divided into two study groups (1 and 2). Root planing was performed using either Gracey curettes (Group 1) or ultrasonic scaler (Group 2). The noncontact profilometer was used to analyze surface roughness before and after root planing. A nanoindenter was used to analyze the surface mechanical properties.
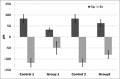
Results: The root planing treatment reduced the peak and valley heights hence decreasing the surface roughness. The average maximum height of peaks (Sp) and average maximum height of valleys (Sv) for control groups remain 83.08 ± 18.47 μm and 117.58 ± 18.02 μm. The Sp was reduced to 32.86 ± 7.99 μm and 62.11 ± 16.07 μm for Groups 1 and 2, respectively. The Sv was reduced to 49.32 ± 29.51 μm for Group 1 and 80.87 ± 17.99 μm Group 2. The nanohardness and modulus of elasticity for cementum of the control group remain 0.28 ± 0.13 GPa and 5.09 ± 2.67 GPa, respectively.
Conclusions: Gracey curettes and ultrasonic scalers are capable of significantly reducing the roughness following root planing. Although Gracey curettes produced smoother surfaces than ultrasonic scalers, there was no significant difference.
Keywords: Biomaterials; cementum; hardness; roughness.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Pihlstrom BL, Michalowicz BS, Johnson NW. Periodontal diseases. Lancet. 2005;366:1809–20. - PubMed
-
- Deas DE, Moritz AJ, Sagun RS, Jr, Gruwell SF, Powell CA. Scaling and root planing vs. conservative surgery in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. Periodontol 2000. 2016;71:128–39. - PubMed
-
- Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Coulthard P, Worthington HV. Enamel matrix derivative (Emdogain) for periodontal tissue regeneration in intrabony defects. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2005. 2005;4:CD003875. - PubMed
-
- Zafar M, Khurshid Z, Almas K. Oral tissue engineering progress and challenges. Tissue Eng Reg Med. 2015;12:387–97.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

