Alpinumisoflavone induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating miR-370/PIM1 signaling
- PMID: 28042498
- PMCID: PMC5199752
Alpinumisoflavone induces apoptosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by modulating miR-370/PIM1 signaling
Abstract
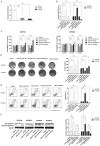
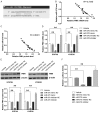
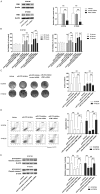
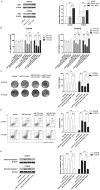
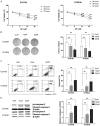
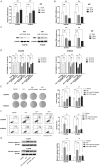
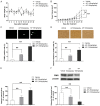
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is the most prevalent type of esophageal cancer and accumulating evidence has confirmed the role of miRNAs in ESCC. One such miRNA, miR-370, was found to be aberrantly downregulated in various human malignancies. This study showed that the expression of miR-370 was significantly lower in ESCC tissues and cell lines, and miR-370 functioned as a tumor suppressor in ESCC. Moreover, this is the first report that showed miR-370 suppresses cell proliferation and tumor growth by directly targeting Pim family kinases 1 (PIM1). Furthermore, alpinumisoflavone, a naturally occurring flavonoid, could inhibit tumor growth of ESCC by targeting miR-370/PIM1 signaling.
Keywords: ESCC; PIM1; alpinumisoflavone; miR-370.
Figures

References
-
- Sakai NS, Samia-Aly E, Barbera M, Fitzgerald RC. A review of the current understanding and clinical utility of miRNAs in esophageal cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2013;23:512–521. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Kim T, Grobmyer SR, Smith R, Ben-David K, Ang D, Vogel SB, Hochwald SN. Esophageal cancer--the five year survivors. J Surg Oncol. 2011;103:179–183. - PubMed
-
- Chen XP, Chen YG, Lan JY, Shen ZJ. MicroRNA-370 suppresses proliferation and promotes endometrioid ovarian cancer chemosensitivity to cDDP by negatively regulating ENG. Cancer Lett. 2014;353:201–210. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
