THE MEASUREMENT OF BONE QUALITY USING GRAY LEVEL CO-OCCURRENCE MATRIX TEXTURAL FEATURES
- PMID: 28042512
- PMCID: PMC5198780
- DOI: 10.1166/jmihi.2016.1812
THE MEASUREMENT OF BONE QUALITY USING GRAY LEVEL CO-OCCURRENCE MATRIX TEXTURAL FEATURES
Abstract
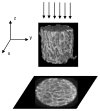
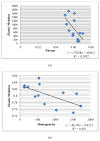
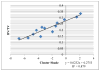
In this paper, statistical methods for the estimation of bone quality to predict the risk of fracture are reported. Bone mineral density and bone architecture properties are the main contributors of bone quality. Dual-energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) is the traditional clinical measurement technique for bone mineral density, but does not include architectural information to enhance the prediction of bone fragility. Other modalities are not practical due to cost and access considerations. This study investigates statistical parameters based on the Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) extracted from two-dimensional projection images and explores links with architectural properties and bone mechanics. Data analysis was conducted on Micro-CT images of 13 trabecular bones (with an in-plane spatial resolution of about 50μm). Ground truth data for bone volume fraction (BV/TV), bone strength and modulus were available based on complex 3D analysis and mechanical tests. Correlation between the statistical parameters and biomechanical test results was studied using regression analysis. The results showed Cluster-Shade was strongly correlated with the microarchitecture of the trabecular bone and related to mechanical properties. Once the principle thesis of utilizing second-order statistics is established, it can be extended to other modalities, providing cost and convenience advantages for patients and doctors.
Keywords: DXA; GLCM; bone; medical imaging; osteoporosis; texture.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Turner C, Rho J, Ashman R, Cowin S. The dependence of elastic constants of cancellous bone upon structural density and fabric. Trans Orthopaed Res Soc. 1988;13:74.
-
- Luo G, Kinney J, Kaufman J, Haupt D, Chiabrera A, Siffert R. Relationship between plain radiographic patterns and three-dimensional trabecular architecture in the human calcaneus. Osteoporosis international. 1999;9:339–345. - PubMed
-
- Benhamou C, Lespessailles E, Jacquet G, Harba R, Jennane R, Loussot T, Tourliere D, Ohley W. Fractal organization of trabecular bone images on calcaneus radiographs. Journal of bone and mineral research. 1994;9:1909–1918. - PubMed
-
- Chappard D, Chennebault A, Moreau M, Legrand E, Audran M, Basle M. Texture analysis of X-ray radiographs is a more reliable descriptor of bone loss than mineral content in a rat model of localized disuse induced by the Clostridium botulinum toxin. Bone. 2001;28:72–79. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
