Incidence and mortality of kidney cancers, and human development index in Asia; a matter of concern
- PMID: 28042551
- PMCID: PMC5106880
- DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2017.06
Incidence and mortality of kidney cancers, and human development index in Asia; a matter of concern
Abstract
Background: The incidence and mortality of kidney cancer have steadily increased by 2%- 3% per decade worldwide, and an increased risk of kidney cancer has been observed in many Asian countries. The information on the incidence and mortality of a disease and its distribution is essential for better planning for prevention and further studies.
Objectives: This study aimed to assess the incidence and mortality of kidney cancer and their correlation with the human development index (HDI) in Asia.
Materials and methods: This ecological study was based on GLOBOCAN data Asia for assessment the correlation between age-specific incidence rate (ASIR) and age-specific mortality rate (ASMR) with HDI and its details that include life expectancy at birth, mean years of schooling and gross national income (GNI) per capita. We use of correlation bivariate method for assessment the correlation between ASIR and ASMR with HDI and its components.
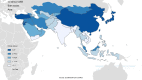
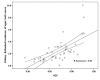
Results: A total of 121 099 kidney cancer cases were recorded in Asian countries in 2012.Overall, 80 080 cases (66.12%) were males. Sex ratio was 1.95. The three countries with the highest number of new patients were china (66 466 cases), Japan (16 830 cases), India(9658 cases), respectively. Positive correlation were seen between HDI and ASIR of kidney cancer 0.655 (P = 0.001), and HDI and ASMR of kidney cancer 0.285 (P = 0.055).
Conclusions: A positive relationship between ASIR and the HDI was seen. The relationship is due to risk factors in countries with high development such as older age, smoking, hypertension, obesity, and diet. However, ASMR showed no significant relationship with HDI.
Keywords: Asia; Human development index; Incidence; Kidney cancer; Mortality.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources