Dose-efficient ultrahigh-resolution scan mode using a photon counting detector computed tomography system
- PMID: 28042589
- PMCID: PMC5177779
- DOI: 10.1117/1.JMI.3.4.043504
Dose-efficient ultrahigh-resolution scan mode using a photon counting detector computed tomography system
Abstract
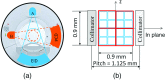
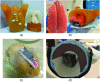
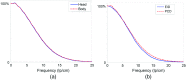
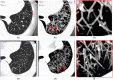
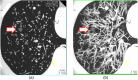
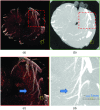
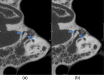
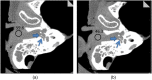
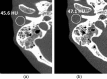
An ultrahigh-resolution (UHR) data collection mode was enabled on a whole-body, research photon counting detector (PCD) computed tomography system. In this mode, 64 rows of [Formula: see text] detector pixels were used, which corresponded to a pixel size of [Formula: see text] at the isocenter. Spatial resolution and image noise were quantitatively assessed for the UHR PCD scan mode, as well as for a commercially available UHR scan mode that uses an energy-integrating detector (EID) and a set of comb filters to decrease the effective detector size. Images of an anthropomorphic lung phantom, cadaveric swine lung, swine heart specimen, and cadaveric human temporal bone were qualitatively assessed. Nearly equivalent spatial resolution was demonstrated by the modulation transfer function measurements: 15.3 and [Formula: see text] spatial frequencies were achieved at 10% and 2% modulation, respectively, for the PCD system and 14.2 and [Formula: see text] for the EID system. Noise was 29% lower in the PCD UHR images compared to the EID UHR images, representing a potential dose savings of 50% for equivalent image noise. PCD UHR images from the anthropomorphic phantom and cadaveric specimens showed clear delineation of small structures.
Keywords: computed tomography; high-resolution mode; photon counting detector; spatial resolution.
Figures


References
-
- Hsieh J., Computed Tomography: Principles, Design, Artifacts, and Recent Advances, SPIE Press, Bellingham, Washington: (2003).
-
- Kalender W. A., Computed Tomography: Fundamentals, System Technology, Image Quality, Applications, 3rd ed., Publicis, Erlangen, Germany: (2011).
-
- Webb W. R., Muller N. L., Naidich D. P., High-Resolution CT of the Lung, 5th ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: (2014).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

