Comparison of Serum rAAV Serotype-Specific Antibodies in Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, Becker Muscular Dystrophy, Inclusion Body Myositis, or GNE Myopathy
- PMID: 28042944
- PMCID: PMC5582585
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2016.141
Comparison of Serum rAAV Serotype-Specific Antibodies in Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, Becker Muscular Dystrophy, Inclusion Body Myositis, or GNE Myopathy
Abstract
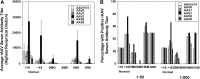
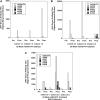
Recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) is a commonly used gene therapy vector for the delivery of therapeutic transgenes in a variety of human diseases, but pre-existing serum antibodies to viral capsid proteins can greatly inhibit rAAV transduction of tissues. Serum was assayed from patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD), inclusion body myositis (IBM), and GNE myopathy (GNE). These were compared to serum from otherwise normal human subjects to determine the extent of pre-existing serum antibodies to rAAVrh74, rAAV1, rAAV2, rAAV6, rAAV8, and rAAV9. In almost all cases, patients with measurable titers to one rAAV serotype showed titers to all other serotypes tested, with average titers to rAAV2 being highest in all instances. Twenty-six percent of all young normal subjects (<18 years old) had measurable rAAV titers to all serotypes tested, and this percentage increased to almost 50% in adult normal subjects (>18 years old). Fifty percent of all IBM and GNE patients also had antibody titers to all rAAV serotypes, while only 18% of DMD and 0% of BMD patients did. In addition, serum-naïve macaques treated systemically with rAAVrh74 could develop cross-reactive antibodies to all other serotypes tested at 24 weeks post treatment. These data demonstrate that most DMD and BMD patients should be amenable to vascular rAAV-mediated treatment without the concern of treatment blockage by pre-existing serum rAAV antibodies, and that serum antibodies to rAAVrh74 are no more common than those for rAAV6, rAAV8, or rAAV9.
Keywords: adeno-associated virus; gene therapy; muscular dystrophy; myopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
rAAVrh74.MCK.
Figures
References
-
- Mingozzi F, High KA. Therapeutic in vivo gene transfer for genetic disease using AAV: progress and challenges. Nat Rev Genet 2011;12:341–355 - PubMed
-
- Spencer HT, Riley BE, Doering CB. State of the art: gene therapy of haemophilia. Haemophilia 2016;22 Suppl 5:66–71 - PubMed
-
- Kalia LV, Kalia SK, Lang AE. Disease-modifying strategies for Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2015;30:1442–1450 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

