High throughput estimation of functional cell activities reveals disease mechanisms and predicts relevant clinical outcomes
- PMID: 28042959
- PMCID: PMC5354899
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.14107
High throughput estimation of functional cell activities reveals disease mechanisms and predicts relevant clinical outcomes
Abstract
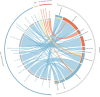
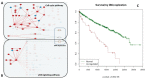
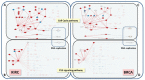
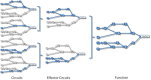
Understanding the aspects of the cell functionality that account for disease or drug action mechanisms is a main challenge for precision medicine. Here we propose a new method that models cell signaling using biological knowledge on signal transduction. The method recodes individual gene expression values (and/or gene mutations) into accurate measurements of changes in the activity of signaling circuits, which ultimately constitute high-throughput estimations of cell functionalities caused by gene activity within the pathway. Moreover, such estimations can be obtained either at cohort-level, in case/control comparisons, or personalized for individual patients. The accuracy of the method is demonstrated in an extensive analysis involving 5640 patients from 12 different cancer types. Circuit activity measurements not only have a high diagnostic value but also can be related to relevant disease outcomes such as survival, and can be used to assess therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: biomarker; disease mechanism; prognostic; signaling pathway; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest
Figures


References
-
- Oti M, Brunner HG. The modular nature of genetic diseases. Clin Genet. 2007;71:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Fey D, Halasz M, Dreidax D, Kennedy SP, Hastings JF, Rauch N, Munoz AG, Pilkington R, Fischer M, Westermann F, Kolch W, Kholodenko BN, Croucher DR. Signaling pathway models as biomarkers: Patient-specific simulations of JNK activity predict the survival of neuroblastoma patients. Sci Signal. 2015;8:ra130. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

