Protease Inhibitors Extracted from Caesalpinia echinata Lam. Affect Kinin Release during Lung Inflammation
- PMID: 28044105
- PMCID: PMC5156802
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/9425807
Protease Inhibitors Extracted from Caesalpinia echinata Lam. Affect Kinin Release during Lung Inflammation
Abstract
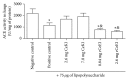
Inflammation is an essential process in many pulmonary diseases in which kinins are generated by protease action on kininogen, a phenomenon that is blocked by protease inhibitors. We evaluated kinin release in an in vivo lung inflammation model in rats, in the presence or absence of CeKI (C. echinata kallikrein inhibitor), a plasma kallikrein, cathepsin G, and proteinase-3 inhibitor, and rCeEI (recombinant C. echinata elastase inhibitor), which inhibits these proteases and also neutrophil elastase. Wistar rats were intravenously treated with buffer (negative control) or inhibitors and, subsequently, lipopolysaccharide was injected into their lungs. Blood, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF), and lung tissue were collected. In plasma, kinin release was higher in the LPS-treated animals in comparison to CeKI or rCeEI groups. rCeEI-treated animals presented less kinin than CeKI-treated group. Our data suggest that kinins play a pivotal role in lung inflammation and may be generated by different enzymes; however, neutrophil elastase seems to be the most important in the lung tissue context. These results open perspectives for a better understanding of biological process where neutrophil enzymes participate and indicate these plant inhibitors and their recombinant correlates for therapeutic trials involving pulmonary diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Using a Caesalpinia echinata Lam. protease inhibitor as a tool for studying the roles of neutrophil elastase, cathepsin G and proteinase 3 in pulmonary edema.Phytochemistry. 2013 Dec;96:235-43. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.09.025. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Phytochemistry. 2013. PMID: 24140156
-
Bioengineering of an elastase inhibitor from Caesalpinia echinata (Brazil wood) seeds.Phytochemistry. 2021 Feb;182:112595. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2020.112595. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Phytochemistry. 2021. PMID: 33321445
-
A proteinase inhibitor from Caesalpinia echinata (pau-brasil) seeds for plasma kallikrein, plasmin and factor XIIa.Biol Chem. 2004 Nov;385(11):1083-6. doi: 10.1515/BC.2004.140. Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15576329
-
Activation of the kallikrein-kinin system and release of new kinins through alternative cleavage of kininogens by microbial and human cell proteinases.Biol Chem. 2004 Nov;385(11):989-96. doi: 10.1515/BC.2004.129. Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15576318 Review.
-
Genetically altered animal models in the kallikrein-kinin system.Biol Chem. 2006 Feb;387(2):119-26. doi: 10.1515/BC.2006.017. Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16497143 Review.
References
-
- Motta G., Rojkjaer R., Hasan A. A. K., Cines D. B., Schmaier A. H. High molecular weight kininogen regulates prekallikrein assembly and activation on endothelial cells: a novel mechanism for contact activation. Blood. 1998;91(2):516–528. - PubMed
-
- Bhoola K. D., Figueroa C. D., Worthy K. Bioregulation of kinins: kallikreins, kininogens, and kininases. Pharmacological Reviews. 1992;44(1):1–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

