Effects of outcome devaluation on instrumental behaviors in a discriminated heterogeneous chain
- PMID: 28045296
- PMCID: PMC5215848
- DOI: 10.1037/xan0000119
Effects of outcome devaluation on instrumental behaviors in a discriminated heterogeneous chain
Abstract
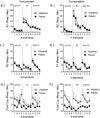
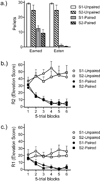
Operant behavior often takes place in a sequence, or chain, of linked responses that lead to a reinforcer. We have recently studied rats performing a discriminated heterogeneous behavior chain that involves the presentation of a discriminative stimulus (e.g., a panel light) to set the occasion for a procurement behavior (e.g., a lever press) that leads to a second stimulus (e.g., a second panel light) that indicates that a consumption response (e.g., a chain pull) will be reinforced. The present study assessed the role played by a representation of the reinforcer in controlling the performance of the responses in this chain. After acquisition of the chain, rats received a reinforcer devaluation treatment in the form of repeated paired, or unpaired, presentations of the food-pellet outcome and lithium-chloride illness. Once paired rats came to reject the pellets, half the animals in each group were tested on procurement, and the other half were tested on consumption. Neither response was affected by the outcome devaluation treatment, although entries into the food cup were suppressed. Combined with other results, the findings suggest that the "goal" for goal-directed procurement responding in a discriminated heterogeneous chain may be the consumption response rather than the primary reinforcer. (PsycINFO Database Record
(c) 2017 APA, all rights reserved).
Figures
References
-
- Adams CD. Variations in the sensitivity of instrumental responding to reinforcer devaluation. Quarterly Journal of Experimental Psychology. 1982;34B:77–98.
-
- Balleine BW. The role of incentive learning in instrumental performance following shifts in primary motivation. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes. 1992;18:236–250. - PubMed
-
- Balleine BW, Garner C, Gonzalez F, Dickinson A. Motivational control of heterogeneous instrumental chains. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Animal Behavior Processes. 1995;21:203–217.
-
- Balleine BW, Paredes-Olay C, Dickinson A. Effects of Outcome Devaluation on the Performance of a Heterogeneous Instrumental Chain. International Journal of Comparative Psychology. 2005;18:257–272.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

