Liver inflammation and fibrosis
- PMID: 28045404
- PMCID: PMC5199698
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI88881
Liver inflammation and fibrosis
Abstract
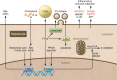
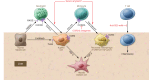
Chronic liver inflammation leads to fibrosis and cirrhosis, which is the 12th leading cause of death in the United States. Hepatocyte steatosis is a component of metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. Hepatic steatosis may be benign or progress to hepatocyte injury and the initiation of inflammation, which activates immune cells. While Kupffer cells are the resident macrophage in the liver, inflammatory cells such as infiltrating macrophages, T lymphocytes, neutrophils, and DCs all contribute to liver inflammation. The inflammatory cells activate hepatic stellate cells, which are the major source of myofibroblasts in the liver. Here we review the initiation of inflammation in the liver, the liver inflammatory cells, and their crosstalk with myofibroblasts.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Health, United States, 2015 Web Site. CDC Web site. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/hus/contents2015.htm#017 Updated April 27, 2016. Accessed November 11, 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

