Grape Polyphenols' Effects in Human Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
- PMID: 28045444
- PMCID: PMC6155751
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22010068
Grape Polyphenols' Effects in Human Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
Abstract
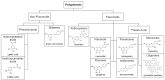
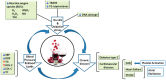
The consumption of fruits and vegetables, as well as foods enriched in bioactive compounds and nutraceuticals, has increased due to consumers' interest in the relevance of food composition for human health. Considerable recent interest has focused on bioactive phenolic compounds in grape, as they possess many biological activities, such as antioxidant, cardioprotective, anticancer, anti-inflammation, anti-ageing and antimicrobial properties. Observational studies indicate that the intake of polyphenol-rich foods improves vascular health, thereby significantly reducing the risk of hypertension, and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Other researchers have described the benefits of a grape polyphenol-rich diet for other types of maladies such as diabetes mellitus. This is a comprehensive review on the consumption of polyphenolic grape compounds, concerning their potential benefits for human health in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Keywords: cardiovascular diseases; dietary antioxidant; grape polyphenols; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Willett W.C., Sacks F., Trichopoulou A., Drescher G., Ferro-Luzzi A., Helsing E., Trichopoulos D. Mediterranean diet pyramid: A cultural model for healthy eating. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995;61:1402S–1406S. - PubMed
-
- Friedman L.A., Kimball A.W. Coronary heart disease mortality and alcohol consumption in framingham. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1986;124:481–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical