Antidepressant responsiveness in adulthood is permanently impaired after neonatal destruction of the neurogenic pool
- PMID: 28045461
- PMCID: PMC5545723
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2016.255
Antidepressant responsiveness in adulthood is permanently impaired after neonatal destruction of the neurogenic pool
Abstract
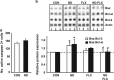
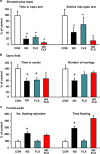
The dynamic turnover of hippocampal neurons is implicated in the regulation of cognitive and affective behavior. Extending our previous demonstration that administration of dexamethasone (ND) to neonatal rats depletes the resident population of neural precursor cells (NPC) and restrains the size of the neurogenic regions, we now show that the adverse effects of ND persist into adulthood. Specifically, ND impairs repletion of the neurogenic pool and neurogenesis; ND also compromises cognitive performance, the ability to actively adapt to an acute stressor and, the efficacy of glucocorticoid (GC) negative feedback. Interestingly, although ND depletes the neurogenic pool, it does not permanently abolish the proliferative machinery of the residual NPC population; however, ND increases the susceptibility of hippocampal granule neurons to apoptosis. Although the antidepressant fluoxetine (FLX) reverses the latter phenomenon, it does not replenish the NPC pool. Treatment of ND-treated adult rats with FLX also improves GC negative feedback, albeit without rescuing the deleterious effects of ND on behavior. In summary, ND leads to protracted disruption of mental functions, some of which are resistant to antidepressant interventions. We conclude that manipulation of the NPC pool during early life may jeopardize the therapeutic potential of antidepressants in adulthood.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Shors TJ. From stem cells to grandmother cells: how neurogenesis relates to learning and memory. Cell Stem Cell 2008; 3: 253–258. - PubMed
-
- Sousa N, Almeida OFX. Disconnection and reconnection: the morphological basis of (mal)adaptation to stress. Trends Neurosci 2012; 35: 742–751. - PubMed
-
- Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH. Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 2008; 132: 645–660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

