Gabapentin for fibromyalgia pain in adults
- PMID: 28045473
- PMCID: PMC6465053
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD012188.pub2
Gabapentin for fibromyalgia pain in adults
Abstract
Background: This review replaces part of an earlier review that evaluated gabapentin for both neuropathic pain and fibromyalgia, now split into separate reviews for the two conditions. This review will consider pain in fibromyalgia only.Fibromyalgia is associated with widespread pain lasting longer than three months, and is frequently associated with symptoms such as poor sleep, fatigue, depression, and reduced quality of life. Fibromyalgia is more common in women.Gabapentin is an antiepileptic drug widely licensed for treatment of neuropathic pain. It is not licensed for the treatment of fibromyalgia, but is commonly used because fibromyalgia can respond to the same medicines as neuropathic pain.
Objectives: To assess the analgesic efficacy of gabapentin for fibromyalgia pain in adults and the adverse events associated with its use in clinical trials.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) via the Cochrane Register of Studies Online, MEDLINE via Ovid and Embase via Ovid from inception to 24 May 2016. We also searched the reference lists of retrieved studies and reviews, and searched online clinical trial registries.
Selection criteria: Randomised, double-blind trials of eight weeks' duration or longer for treating fibromyalgia pain in adults, comparing gabapentin with placebo or an active comparator.
Data collection and analysis: Two independent review authors extracted data and assessed trial quality and risk of bias. We planned to use dichotomous data to calculate risk ratio and number needed to treat for one additional event, using standard methods. We assessed the evidence using GRADE (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation) and created a 'Summary of findings' table.
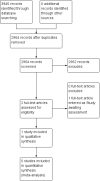
Main results: Two studies tested gabapentin to treat fibromyalgia pain. One was identified in previous versions of the review and is included here. We identified another study as a conference abstract, with insufficient detail to determine eligibility for inclusion; it is awaiting assessment. The one included study of 150 participants was a 12-week, multi-centre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study using last-observation-carried-forward imputation for withdrawals. The maximum dose was 2400 mg daily. The overall risk of bias was low, except for attrition bias.At the end of the trial, the outcome of 50% reduction in pain over baseline was not reported. The outcome of 30% or greater reduction in pain over baseline was achieved by 38/75 participants (49%) with gabapentin compared with 23/75 (31%) with placebo (very low quality). A patient global impression of change any category of "better" was achieved by 68/75 (91%) with gabapentin and 35/75 (47%) with placebo (very low quality).Nineteen participants discontinued the study because of adverse events: 12 in the gabapentin group (16%) and 7 in the placebo group (9%) (very low quality). The number of serious adverse events were not reported, and no deaths were reported (very low quality).
Authors' conclusions: We have only very low quality evidence and are very uncertain about estimates of benefit and harm because of a small amount of data from a single trial. There is insufficient evidence to support or refute the suggestion that gabapentin reduces pain in fibromyalgia.
Conflict of interest statement
TC: none known.
SD: none known.
PW: none known.
RAM has received grant support from Grünenthal relating to individual patient level analyses of trial data regarding tapentadol in osteoarthritis and back pain (2015). He has received honoraria for attending boards with Menarini concerning methods of analgesic trial design (2014), with Novartis (2014) about the design of network meta‐analyses, and RB on understanding pharmacokinetics of drug uptake (2015). He has received honoraria from Omega Pharma (2016) and Futura Pharma (2016) for providing advice on trial and data analysis methods.
Figures
Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Arnold 2007 {published data only}
References to studies awaiting assessment
Mouzopoulos 2014 {published data only}
-
- Mouzopoulos G, Tsembeli A, Skevofilax I, Nomikos G, Vasiliadis V. Duloxetine is superior to gabapentin in the treatment of the fibromyalgia. Pain Practice. Blackwell Publishing Inc, 2014; Vol. 14:45.
Additional references
Arnold 2013
Backonja 2011
Bennett 2007
Boyle 2014
Bradley 2009
Chang 2014
Choi 2010
Clauw 2014
Cording 2015
Dworkin 2008
Eich 2012
EMC 2009
-
- Electronic Medicines Compendium. http://emc.medicines.org.uk/ (accessed 1 May 2009).
EPOC 2015
-
- Effective Practice, Organisation of Care (EPOC). 23. Worksheets for preparing a Summary of Findings using GRADE. Resources for review authors. Oslo: Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services Available at: http://epoc.cochrane.org/epoc‐specific‐resources‐review‐authors (accessed 30 November 2016) 2015.
Eroglu 2009
Fitzcharles 2013
Forseth 1999
-
- Forseth KO, Husby G, Gran JT, Førre O. Prognostic factors for the development of fibromyalgia in women with self‐reported musculoskeletal pain. A prospective study. Journal of Rheumatology 1999;26:2458‐67. [PUBMED: 10555910] - PubMed
Guyatt 2013a
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Sultan S, Brozek J, Glasziou P, Alonso‐Coello P, et al. GRADE guidelines: 11. Making an overall rating of confidence in effect estimates for a single outcome and for all outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013;66(2):151‐7. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2012.01.006] - DOI - PubMed
Guyatt 2013b
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hoffman 2010
Häuser 2009
Häuser 2011
Häuser 2013a
-
- Häuser W, Galek A, Erbslöh‐Möller B, Köllner V, Kühn‐Becker H, Langhorst J, et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder in fibromyalgia syndrome: prevalence, temporal relationship between posttraumatic stress and fibromyalgia symptoms, and impact on clinical outcome. Pain 2013;154:1216‐23. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2013.03.034] - DOI - PubMed
Häuser 2013b
Häuser 2014
Häuser 2015
Jadad 1996
Kalso 2013
Koroschetz 2011
L'Abbé 1987
-
- L'Abbé KA, Detsky AS, O'Rourke K. Meta‐analysis in clinical research. Annals of Internal Medicine 1987;107(2):224‐33. - PubMed
Landefeld 2009
Lange 2010
Lee 2012
Lunn 2014
Macfarlane 2016
Mansfield 2016
McQuay 1998
-
- McQuay H, Moore R. An Evidence‐based Resource for Pain Relief. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998. [ISBN: 0‐19‐263048‐2]
Moore 1998
Moore 2008
-
- Moore RA, Barden J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Managing potential publication bias. In: McQuay HJ, Kalso E, Moore RA editor(s). Systematic Reviews in Pain Research: Methodology Refined. Seattle: IASP Press, 2008:15‐24. [ISBN: 978–0–931092–69–5]
Moore 2008b
-
- Moore RA, Gavaghan D, Tramèr MR, Collins SL, McQuay HJ. Size is everything‐‐large amounts of information are needed to overcome random effects in estimating direction and magnitude of treatment effects. Pain 1998;78(3):209‐16. - PubMed
Moore 2009
Moore 2010a
Moore 2010b
Moore 2010c
-
- Moore RA, Moore OA, Derry S, Peloso PM, Gammaitoni AR, Wang H. Responder analysis for pain relief and numbers needed to treat in a meta‐analysis of etoricoxib osteoarthritis trials: bridging a gap between clinical trials and clinical practice. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 2010;69(2):374‐9. [DOI: 10.1136/ard.2009.107805] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Moore 2010d
Moore 2011b
-
- Moore RA, Straube S, Paine J, Derry S, McQuay HJ. Minimum efficacy criteria for comparisons between treatments using individual patient meta‐analysis of acute pain trials: examples of etoricoxib, paracetamol, ibuprofen, and ibuprofen/paracetamol combinations after third molar extraction. Pain 2011;152(5):982‐9. [DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2010.11.030] - DOI - PubMed
Moore 2011c
Moore 2012a
Moore 2012b
Moore 2013a
Moore 2013b
Moore 2014b
-
- Moore RA, Derry S, Taylor RS, Straube S, Phillips CJ. The costs and consequences of adequately managed chronic non‐cancer pain and chronic neuropathic pain. Pain Practice 2014;14(1):79‐94. - PubMed
Moore 2014c
Moore 2015
Mork 2010
O'Brien 2010
Oaklander 2013
PaPaS 2012
-
- Cochrane Pain, Palliative and Supportive Care Group. PaPaS author and referee guidance. http://papas.cochrane.org/papas‐documents (accessed 17 August 2015).
Queiroz 2013
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Sang 2013
Sommer 2012
Straube 2008
-
- Straube S, Derry S, McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Enriched enrolment: definition and effects of enrichment and dose in trials of pregabalin and gabapentin in neuropathic pain. A systematic review. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2008;66(2):266‐75. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2008.03200.x] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Straube 2010
Straube 2011
Sultan 2008
Tzellos 2010
-
- Tzellos TG, Toulis KA, Goulis DG, Papazisis G, Zampeli VA, Vakfari A, et al. Gabapentin and pregabalin in the treatment of fibromyalgia: a systematic review and a meta‐analysis. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2010;35(6):239‐56. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01144.x] - DOI - PubMed
Vedula 2009
Vos 2012
-
- Vos T, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Lozano R, Michaud C, Ezzati M, et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012;380(9859):2163‐96. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Walitt 2015
Wiffen 2000
Wiffen 2005
Wiffen 2013
Wolfe 1990
-
- Wolfe F, Smythe HA, Yunus MB, Bennett RM, Bombardier C, Goldenberg DL, et al. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 Criteria for the Classification of Fibromyalgia. Report of the Multicenter Criteria Committee. Arthritis and Rheumatism 1990;33(2):160‐72. - PubMed
Wolfe 2010
Wolfe 2011
-
- Wolfe F, Clauw DJ, Fitzcharles MA, Goldenberg DL, Häuser W, Katz RS, et al. Fibromyalgia criteria and severity scales for clinical and epidemiological studies: a modification of the ACR Preliminary Diagnostic Criteria for Fibromyalgia. Journal of Rheumatology 2011;38:1113‐22. [DOI: 10.3899/jrheum.100594] - DOI - PubMed
Wolfe 2013
Wolfe 2014
Yunus 2008
Üçeyler 2013a
References to other published versions of this review
Moore 2011a
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical