Some Neurocognitive Correlates of Noise-Vocoded Speech Perception in Children With Normal Hearing: A Replication and Extension of )
- PMID: 28045787
- PMCID: PMC5404985
- DOI: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000393
Some Neurocognitive Correlates of Noise-Vocoded Speech Perception in Children With Normal Hearing: A Replication and Extension of )
Abstract
Objectives: Noise-vocoded speech is a valuable research tool for testing experimental hypotheses about the effects of spectral degradation on speech recognition in adults with normal hearing (NH). However, very little research has utilized noise-vocoded speech with children with NH. Earlier studies with children with NH focused primarily on the amount of spectral information needed for speech recognition without assessing the contribution of neurocognitive processes to speech perception and spoken word recognition. In this study, we first replicated the seminal findings reported by ) who investigated effects of lexical density and word frequency on noise-vocoded speech perception in a small group of children with NH. We then extended the research to investigate relations between noise-vocoded speech recognition abilities and five neurocognitive measures: auditory attention (AA) and response set, talker discrimination, and verbal and nonverbal short-term working memory.
Design: Thirty-one children with NH between 5 and 13 years of age were assessed on their ability to perceive lexically controlled words in isolation and in sentences that were noise-vocoded to four spectral channels. Children were also administered vocabulary assessments (Peabody Picture Vocabulary test-4th Edition and Expressive Vocabulary test-2nd Edition) and measures of AA (NEPSY AA and response set and a talker discrimination task) and short-term memory (visual digit and symbol spans).
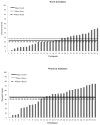
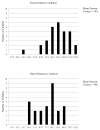
Results: Consistent with the findings reported in the original ) study, we found that children perceived noise-vocoded lexically easy words better than lexically hard words. Words in sentences were also recognized better than the same words presented in isolation. No significant correlations were observed between noise-vocoded speech recognition scores and the Peabody Picture Vocabulary test-4th Edition using language quotients to control for age effects. However, children who scored higher on the Expressive Vocabulary test-2nd Edition recognized lexically easy words better than lexically hard words in sentences. Older children perceived noise-vocoded speech better than younger children. Finally, we found that measures of AA and short-term memory capacity were significantly correlated with a child's ability to perceive noise-vocoded isolated words and sentences.
Conclusions: First, we successfully replicated the major findings from the ) study. Because familiarity, phonological distinctiveness and lexical competition affect word recognition, these findings provide additional support for the proposal that several foundational elementary neurocognitive processes underlie the perception of spectrally degraded speech. Second, we found strong and significant correlations between performance on neurocognitive measures and children's ability to recognize words and sentences noise-vocoded to four spectral channels. These findings extend earlier research suggesting that perception of spectrally degraded speech reflects early peripheral auditory processes, as well as additional contributions of executive function, specifically, selective attention and short-term memory processes in spoken word recognition. The present findings suggest that AA and short-term memory support robust spoken word recognition in children with NH even under compromised and challenging listening conditions. These results are relevant to research carried out with listeners who have hearing loss, because they are routinely required to encode, process, and understand spectrally degraded acoustic signals.
Figures
References
-
- Bates TC, D’Oliveiro L. PsyScript: A Macintosh application for scripting experiments. Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers. 2003;35(4):565–576. - PubMed
-
- Bell TS, Wilson RH. Sentence recognition materials based on frequency of word use and lexical confusability. Journal of the American Academy of Audiology. 2001;12(10):514–522. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

