A Rough Set Bounded Spatially Constrained Asymmetric Gaussian Mixture Model for Image Segmentation
- PMID: 28045950
- PMCID: PMC5207730
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168449
A Rough Set Bounded Spatially Constrained Asymmetric Gaussian Mixture Model for Image Segmentation
Abstract
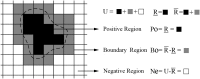
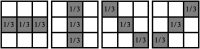
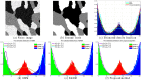
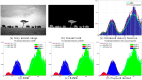
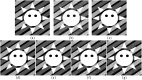
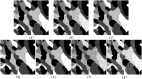
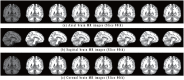
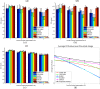
Accurate image segmentation is an important issue in image processing, where Gaussian mixture models play an important part and have been proven effective. However, most Gaussian mixture model (GMM) based methods suffer from one or more limitations, such as limited noise robustness, over-smoothness for segmentations, and lack of flexibility to fit data. In order to address these issues, in this paper, we propose a rough set bounded asymmetric Gaussian mixture model with spatial constraint for image segmentation. First, based on our previous work where each cluster is characterized by three automatically determined rough-fuzzy regions, we partition the target image into three rough regions with two adaptively computed thresholds. Second, a new bounded indicator function is proposed to determine the bounded support regions of the observed data. The bounded indicator and posterior probability of a pixel that belongs to each sub-region is estimated with respect to the rough region where the pixel lies. Third, to further reduce over-smoothness for segmentations, two novel prior factors are proposed that incorporate the spatial information among neighborhood pixels, which are constructed based on the prior and posterior probabilities of the within- and between-clusters, and considers the spatial direction. We compare our algorithm to state-of-the-art segmentation approaches in both synthetic and real images to demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed algorithm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




References
-
- Wen XZ, Shao L, Xue Y, Fang W A rapid learning algorithm for vehicle classification. Information Sciences. 2015. February;295(1):395–406. 10.1016/j.ins.2014.10.040 - DOI
-
- Gu B, Sheng VS, Li S. Bi-parameter space partition for cost-sensitive SVM. Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence. AAAI Press. 2015:3532–3539.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

