RNA Sequencing Reveals that Kaposi Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection Mimics Hypoxia Gene Expression Signature
- PMID: 28046107
- PMCID: PMC5234848
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006143
RNA Sequencing Reveals that Kaposi Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus Infection Mimics Hypoxia Gene Expression Signature
Abstract
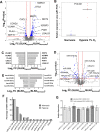
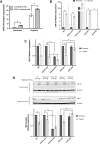
Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) causes several tumors and hyperproliferative disorders. Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) activate latent and lytic KSHV genes, and several KSHV proteins increase the cellular levels of HIF. Here, we used RNA sequencing, qRT-PCR, Taqman assays, and pathway analysis to explore the miRNA and mRNA response of uninfected and KSHV-infected cells to hypoxia, to compare this with the genetic changes seen in chronic latent KSHV infection, and to explore the degree to which hypoxia and KSHV infection interact in modulating mRNA and miRNA expression. We found that the gene expression signatures for KSHV infection and hypoxia have a 34% overlap. Moreover, there were considerable similarities between the genes up-regulated by hypoxia in uninfected (SLK) and in KSHV-infected (SLKK) cells. hsa-miR-210, a HIF-target known to have pro-angiogenic and anti-apoptotic properties, was significantly up-regulated by both KSHV infection and hypoxia using Taqman assays. Interestingly, expression of KSHV-encoded miRNAs was not affected by hypoxia. These results demonstrate that KSHV harnesses a part of the hypoxic cellular response and that a substantial portion of hypoxia-induced changes in cellular gene expression are induced by KSHV infection. Therefore, targeting hypoxic pathways may be a useful way to develop therapeutic strategies for KSHV-related diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Next-Generation Sequencing Analysis Reveals Differential Expression Profiles of MiRNA-mRNA Target Pairs in KSHV-Infected Cells.PLoS One. 2015 May 5;10(5):e0126439. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126439. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25942495 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Cross-Linking, Ligation, and Sequencing of Hybrids (qCLASH) Identifies Kaposi's Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus MicroRNA Targets in Endothelial Cells.J Virol. 2018 Mar 28;92(8):e02138-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02138-17. Print 2018 Apr 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29386283 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of KAP1 enhances hypoxia-induced Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus reactivation through RBP-Jκ.J Virol. 2014 Jun;88(12):6873-84. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00283-14. Epub 2014 Apr 2. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24696491 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection and disease pathogenesis.J Med Virol. 2023 Sep;95(9):e29071. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29071. J Med Virol. 2023. PMID: 37665216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNAs and their roles in KSHV pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2019 Jun;266:15-24. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2019.03.024. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Virus Res. 2019. PMID: 30951791 Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic reprogramming of Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpes virus infected B-cells in hypoxia.PLoS Pathog. 2018 May 10;14(5):e1007062. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007062. eCollection 2018 May. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29746587 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-associated Kaposi sarcoma and related diseases.AIDS. 2017 Sep 10;31(14):1903-1916. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001567. AIDS. 2017. PMID: 28609402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High levels of LINE-1 transposable elements expressed in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-related primary effusion lymphoma.Oncogene. 2021 Jan;40(3):536-550. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-01549-9. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 33188297
-
A role of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in Murine Gammaherpesvirus 68 (MHV68) lytic replication and reactivation from latency.PLoS Pathog. 2019 Dec 6;15(12):e1008192. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008192. eCollection 2019 Dec. PLoS Pathog. 2019. PMID: 31809522 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Causality of Human Cancer and Potential Roles of Human Endogenous Retroviruses in the Multi-Omics Era: An Evolutionary Epidemiology Review.Front Oncol. 2021 Oct 29;11:687631. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.687631. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34778024 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cesarman E, Moore PS, Rao PH, Inghirami G, Knowles DM, Chang Y. In vitro establishment and characterization of two acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related lymphoma cell lines (BC-1 and BC-2) containing Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like (KSHV) DNA sequences. Blood. American Society of Hematology; 1995;86: 2708–14. - PubMed
-
- Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E, Cacoub P, Cazals-Hatem D, Babinet P, et al. Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman’s disease. Blood. American Society of Hematology; 1995;86: 1276–80. - PubMed
-
- Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, Lee F, Culpepper J, Knowles DM, et al. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi’s sarcoma. Science (80-). 1994;266: 1865–1869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

