Glutamate transporter type 3 participates in maintaining morphine-induced conditioned place preference
- PMID: 28049029
- PMCID: PMC5303644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.12.038
Glutamate transporter type 3 participates in maintaining morphine-induced conditioned place preference
Abstract
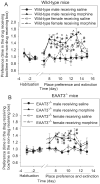
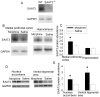
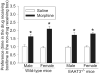
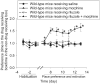
Glutamate transporters (EAAT) have been implicated in the drug addiction behavior. We determined whether EAAT type 3 (EAAT3) played a role in morphine addiction. Six- to eight-week-old EAAT3 knockout (EAAT3-/-) mice and their wild-type littermates received 3 intraperitoneal injections of 10mg/kg morphine, each on an alternative day, to induce conditioned place preference (CPP). Two days after the place preference returned to baseline, mice received 2.5mg/kg morphine to induce reinstatement. Some mice received intraperitoneal injection of 4mg/kg riluzole, an EAAT activator, 30min before morphine or saline injection. Hippocampus, medial prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area were harvested for Western analysis 24h after the last dose of morphine was injected. Morphine induced CPP in wild-type and EAAT3-/- mice. Gender is not a statistically significant factor to influence this behavior. This conditioned behavior extinguished after morphine administration was stopped for 8-9days in wild-type mice, while this extinction occurred 6days after discontinuation of morphine injection in EAAT3-/- mice. A small dose of morphine similarly reinstated the conditioned behavior in the wild-type and EAAT3-/- mice. Riluzole abolished morphine-induced CPP during the initial place preference. Morphine increased EAAT3 expression in the plasma membrane of medial prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area but did not affect EAAT3 expression in the hippocampus. These results suggest that EAAT3 delays the extinction of morphine-induced CPP. EAAT activation may prevent the formation of morphine-induced CPP.
Keywords: conditioned place preference; glutamate transporter; mice; morphine.
Copyright © 2016 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Aoyama K, Suh SW, Hamby AM, Liu J, Chan WY, Chen Y, Swanson RA. Neuronal glutathione deficiency and age-dependent neurodegeneration in the EAAC1 deficient mouse. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Cao MN, Zhou YB, Gao AH, Cao JY, Gao LX, Sheng L, Xu L, Su MB, Cao XC, Han MM, Wang MK, Li J. Curcusone D, a novel ubiquitin-proteasome pathway inhibitor via ROS-induced DUB inhibition, is synergistic with bortezomib against multiple myeloma cell growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014;1840:2004–2013. - PubMed
-
- Cheah BC, Vucic S, Krishnan AV, Kiernan MC. Riluzole, neuroprotection and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Curr Med Chem. 2010;17:1942–1199. - PubMed
-
- Daglish MR, Weinstein A, Malizia AL, Wilson S, Melichar JK, Britten S, Brewer C, Lingford-Hughes A, Myles JS, Grasby P, Nutt DJ. Changes in regional cerebral blood flow elicited by craving memories in abstinent opiate-dependent subjects. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158:1680–1686. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

