Interstitial Lung Disease Induced by Pazopanib Treatment
- PMID: 28050004
- PMCID: PMC5313429
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.56.7380
Interstitial Lung Disease Induced by Pazopanib Treatment
Abstract
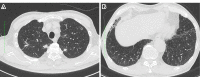
Although pneumothorax has been reported to be a major pulmonary adverse event in patients treated with pazopanib, a multikinase inhibitor, drug-induced interstitial lung disease (DILD) has not been reported. A 74-year-old Japanese man who received pazopanib for the treatment of femoral leiomyosarcoma and lung metastasis presented with dyspnea and fatigue. He had mild interstitial pneumonia when pazopanib treatment was initiated. Chest computed tomography revealed progressive bilateral ground-glass opacity (GGO) and traction bronchiectasis. We diagnosed DILD due to pazopanib. The patient's pazopanib treatment was interrupted and a steroid was administered. The symptoms and GGO were improved with treatment. Physicians should be aware of DILD due to pazopanib in patients with pre-existing interstitial lung disease.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pazopanib-associated interstitial lung disease in a patient with renal cell carcinoma.BMJ Case Rep. 2020 Jul 8;13(7):e235177. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-235177. BMJ Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32641305 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma with Long-Term Disease Control by Pazopanib.Kobe J Med Sci. 2016 Jul 5;62(2):E45-8. Kobe J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27578036 Free PMC article.
-
Promising effects of pazopanib with radiation on an advanced prostate leiomyosarcoma after failure of systemic chemotherapy.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019 May;35(5):317-318. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12035. Epub 2019 Mar 19. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30887661 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pazopanib-induced fatal heart failure in a patient with unresectable soft tissue sarcoma and review of literature.J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020 Apr;26(3):768-774. doi: 10.1177/1078155219875797. Epub 2019 Sep 23. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 2020. PMID: 31547750 Review.
-
Drug-induced interstitial lung disease caused by olaparib: three case reports and review of the Japanese Adverse Drug Event Report database and literature.BMC Pulm Med. 2023 Aug 8;23(1):289. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02569-3. BMC Pulm Med. 2023. PMID: 37553592 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pazopanib-associated interstitial lung disease in a patient with renal cell carcinoma.BMJ Case Rep. 2020 Jul 8;13(7):e235177. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-235177. BMJ Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32641305 Free PMC article.
-
Pazopanib-induced organizing pneumonia in a patient with leiomyosarcoma: A case report.Respir Med Case Rep. 2020 May 31;30:101112. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101112. eCollection 2020. Respir Med Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32528844 Free PMC article.
-
Fatal interstitial lung disease associated with a series of tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatment in a non-small cell lung cancer patient: a case report.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 May;9(5):3762-3765. doi: 10.21037/tcr.2020.03.76. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117740 Free PMC article.
-
Regorafenib Induced Interstitial Pneumonia in a Patient With Refractory Rectal Cancer.Respirol Case Rep. 2025 Jul 30;13(8):e70286. doi: 10.1002/rcr2.70286. eCollection 2025 Aug. Respirol Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40746636 Free PMC article.
-
Drug-Related Pneumonitis in Cancer Treatment during the COVID-19 Era.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 2;13(5):1052. doi: 10.3390/cancers13051052. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801385 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schutz FA, Choueiri TK, Sternberg CN. Pazopanib: clinical development of a potent anti-angiogenic drug. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 77: 163-171, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, et al. . Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol 28: 1061-1068, 2010. - PubMed
-
- van der Graaf WT, Blay JY, Chawla SP, et al. . Pazopanib for metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma (PALETTE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 379: 1879-1886, 2012. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

