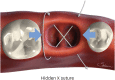
The hidden X suture: a technical note on a novel suture technique for alveolar ridge preservation
- PMID: 28050319
- PMCID: PMC5200867
- DOI: 10.5051/jpis.2016.46.6.415
The hidden X suture: a technical note on a novel suture technique for alveolar ridge preservation
Abstract
Purpose: The present study investigated the impact of 2 different suture techniques, the conventional crossed mattress suture (X suture) and the novel hidden X suture, for alveolar ridge preservation (ARP) with an open healing approach.
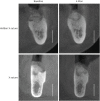
Methods: This study was a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Fourteen patients requiring extraction of the maxillary or mandibular posterior teeth were enrolled and allocated into 2 groups. After extraction, demineralized bovine bone matrix mixed with 10% collagen (DBBM-C) was grafted and the socket was covered by porcine collagen membrane in a double-layer fashion. No attempt to obtain primary closure was made. The hidden X suture and conventional X suture techniques were performed in the test and control groups, respectively. Cone-beam computed tomographic (CBCT) images were taken immediately after the graft procedure and before implant surgery 4 months later. Additionally, the change in the mucogingival junction (MGJ) position was measured and was compared after extraction, after suturing, and 4 months after the operation.
Results: All sites healed without any complications. Clinical evaluations showed that the MGJ line shifted to the lingual side immediately after the application of the X suture by 1.56±0.90 mm in the control group, while the application of the hidden X suture rather pushed the MGJ line slightly to the buccal side by 0.25±0.66 mm. It was demonstrated that the amount of keratinized tissue (KT) preserved on the buccal side was significantly greater in the hidden X suture group 4 months after the procedure (P<0.05). Radiographic analysis showed that the hidden X suture had a significant effect in preserving horizontal width and minimizing vertical reduction in comparison to X suture (P<0.05).
Conclusions: Our study provided clinical and radiographic verification of the efficacy of the hidden X suture in preserving the width of KT and the dimensions of the alveolar ridge after ARP.
Keywords: Alveolar process; Bone regeneration; Bone resorption; Suture techniques; Tooth extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



References
-
- Schropp L, Wenzel A, Kostopoulos L, Karring T. Bone healing and soft tissue contour changes following single-tooth extraction: a clinical and radiographic 12-month prospective study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2003;23:313–323. - PubMed
-
- Wang RE, Lang NP. Ridge preservation after tooth extraction. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(Suppl 6):147–156. - PubMed
-
- Araújo MG, Liljenberg B, Lindhe J. Dynamics of Bio-Oss Collagen incorporation in fresh extraction wounds: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21:55–64. - PubMed
-
- Araújo MG, Lindhe J. Ridge preservation with the use of Bio-Oss collagen: a 6-month study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2009;20:433–440. - PubMed
-
- Fickl S, Zuhr O, Wachtel H, Bolz W, Huerzeler MB. Hard tissue alterations after socket preservation: an experimental study in the beagle dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2008;19:1111–1118. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

