The histone 3 lysine 9 methyltransferase inhibitor chaetocin improves prognosis in a rat model of high salt diet-induced heart failure
- PMID: 28051130
- PMCID: PMC5209701
- DOI: 10.1038/srep39752
The histone 3 lysine 9 methyltransferase inhibitor chaetocin improves prognosis in a rat model of high salt diet-induced heart failure
Abstract
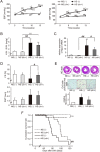
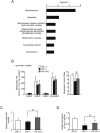
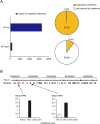
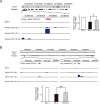
Histone acetylation has been linked to cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. However, the pathological implications of changes in histone methylation and the effects of interventions with histone methyltransferase inhibitors for heart failure have not been fully clarified. Here, we focused on H3K9me3 status in the heart and investigated the effects of the histone H3K9 methyltransferase inhibitor chaetocin on prognoses in Dahl salt-sensitive rats, an animal model of chronic heart failure. Chaetocin prolonged survival and restored mitochondrial dysfunction. ChIP-seq analysis demonstrated that chronic stress to the heart induced H3K9me3 elevation in thousands of repetitive elements, including intronic regions of mitochondria-related genes, such as the gene encoding peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 alpha. Furthermore, chaetocin reversed this effect on these repetitive loci. These data suggested that excessive heterochromatinization of repetitive elements of mitochondrial genes in the failing heart may lead to the silencing of genes and impair heart function. Thus, chaetocin may be a potential therapeutic agent for chronic heart failure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of histone methyltransferase inhibitor chaetocin on histone H3K9 methylation of cultured ovine somatic cells and development of preimplantation cloned embryos.Reprod Toxicol. 2018 Aug;79:124-131. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2018.06.006. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Reprod Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29909068
-
High Glucose Increases the Expression of Inflammatory Cytokine Genes in Macrophages Through H3K9 Methyltransferase Mechanism.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016 Jan;36(1):48-61. doi: 10.1089/jir.2014.0172. Epub 2015 Sep 25. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2016. PMID: 26406561
-
Chaetocin-A histone methyltransferase inhibitor-Impairs proliferation, arrests cell cycle and induces nucleolar disassembly in Trypanosoma cruzi.Acta Trop. 2017 Jun;170:149-160. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Feb 6. Acta Trop. 2017. PMID: 28185826
-
Epigenetic landscape of amphetamine and methamphetamine addiction in rodents.Epigenetics. 2015;10(7):574-80. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2015.1055441. Epigenetics. 2015. PMID: 26023847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chromatin modifications remodel cardiac gene expression.Cardiovasc Res. 2014 Jul 1;103(1):7-16. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu122. Epub 2014 May 8. Cardiovasc Res. 2014. PMID: 24812277 Review.
Cited by
-
The Smyd Family of Methyltransferases: Role in Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Physiology and Pathology.Curr Opin Physiol. 2018 Feb;1:140-152. doi: 10.1016/j.cophys.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Dec 13. Curr Opin Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29435515 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation in cardiovascular disease: mechanisms and advances in clinical trials.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jun 25;7(1):200. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01055-2. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35752619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Silico Analysis of Differential Gene Expression in Three Common Rat Models of Diastolic Dysfunction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018 Feb 21;5:11. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2018.00011. eCollection 2018. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018. PMID: 29556499 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging epigenetic therapies of cardiac fibrosis and remodelling in heart failure: from basic mechanisms to early clinical development.Cardiovasc Res. 2023 Feb 3;118(18):3482-3498. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvac142. Cardiovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 36004821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting KDM4C Prevents Heart Failure after Acute Myocardial Infarction Via Activation of SOS2.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025 Jun;18(3):498-511. doi: 10.1007/s12265-025-10594-2. Epub 2025 Feb 3. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39900886
References
-
- Gaddam K. K. & Ventura H. Developments in heart failure 2011. Congest Heart Fail 18, 112–126 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Packer M. et al.. The effect of carvedilol on morbidity and mortality in patients with chronic heart failure. U.S. Carvedilol Heart Failure Study Group. N Engl J Med 334, 1349–1355 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Packer M. et al.. Effect of carvedilol on survival in severe chronic heart failure. N Engl J Med 344, 1651–1658 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Effect of metoprolol CR/XL in chronic heart failure: Metoprolol CR/XL randomised intervention trial in congestive heart failure (MERIT-HF). MERIT-HF Study Group. Lancet 353, 2001–2007 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

