CRL4WDR1 Controls Polo-like Kinase Protein Abundance to Promote Bilobe Duplication, Basal Body Segregation and Flagellum Attachment in Trypanosoma brucei
- PMID: 28052114
- PMCID: PMC5241021
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006146
CRL4WDR1 Controls Polo-like Kinase Protein Abundance to Promote Bilobe Duplication, Basal Body Segregation and Flagellum Attachment in Trypanosoma brucei
Abstract
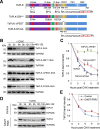
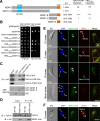
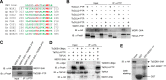
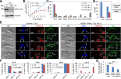
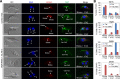
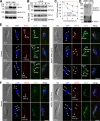
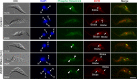
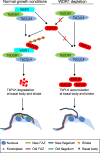
The Polo-like kinase homolog in Trypanosoma brucei, TbPLK, plays essential roles in basal body segregation, flagellum attachment and cytokinesis. The level of TbPLK protein is tightly controlled, but the underlying mechanism remains elusive. Here, we report a Cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase composed of Cullin4, the DNA damage-binding protein 1 homolog TbDDB1 and a WD40-repeat protein WDR1 that controls TbPLK abundance in the basal body and the bilobe. WDR1, through its C-terminal domain, interacts with the PEST motif in TbPLK and, through its N-terminal WD40 motif, binds to TbDDB1. Depletion of WDR1 inhibits bilobe duplication and basal body segregation, disrupts the assembly of the new flagellum attachment zone filament and detaches the new flagellum. Consistent with its role in TbPLK degradation, depletion of WDR1 causes excessive accumulation of TbPLK in the basal body and the bilobe, leading to continuous phosphorylation of TbCentrin2 in the bilobe at late cell cycle stages. Together, these results identify a novel WD40-repeat protein as a TbPLK receptor in the Cullin4-DDB1 ubiquitin ligase complex for degrading TbPLK in the basal body and the bilobe after the G1/S cell cycle transition, thereby promoting bilobe duplication, basal body separation and flagellum-cell body adhesion.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Novel Basal Body Protein That Is a Polo-like Kinase Substrate Is Required for Basal Body Segregation and Flagellum Adhesion in Trypanosoma brucei.J Biol Chem. 2015 Oct 9;290(41):25012-22. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.674796. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26272611 Free PMC article.
-
Polo-like kinase phosphorylation of bilobe-resident TbCentrin2 facilitates flagellar inheritance in Trypanosoma brucei.Mol Biol Cell. 2013 Jun;24(12):1947-63. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-12-0911. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23615446 Free PMC article.
-
Flagellum inheritance in Trypanosoma brucei requires a kinetoplastid-specific protein phosphatase.J Biol Chem. 2018 Jun 1;293(22):8508-8520. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002106. Epub 2018 Apr 17. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29666191 Free PMC article.
-
The Flagellum Attachment Zone: 'The Cellular Ruler' of Trypanosome Morphology.Trends Parasitol. 2016 Apr;32(4):309-324. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2015.12.010. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Trends Parasitol. 2016. PMID: 26776656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assembly of the flagellum and its role in cell morphogenesis in Trypanosoma brucei.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010 Aug;13(4):453-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2010.05.006. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20541452 Review.
Cited by
-
WDR2 regulates the orphan kinesin KIN-G to promote hook complex and Golgi biogenesis in Trypanosoma brucei.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 29:2025.01.29.635568. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.29.635568. bioRxiv. 2025. Update in: mBio. 2025 Jul 9;16(7):e0037125. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00371-25. PMID: 39975200 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
A functional analysis of TOEFAZ1 uncovers protein domains essential for cytokinesis in Trypanosoma brucei.J Cell Sci. 2017 Nov 15;130(22):3918-3932. doi: 10.1242/jcs.207209. Epub 2017 Oct 9. J Cell Sci. 2017. PMID: 28993462 Free PMC article.
-
TbSmee1 regulates hook complex morphology and the rate of flagellar pocket uptake in Trypanosoma brucei.Mol Microbiol. 2018 Feb;107(3):344-362. doi: 10.1111/mmi.13885. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Mol Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29178204 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitination and the Proteasome as Drug Targets in Trypanosomatid Diseases.Front Chem. 2021 Jan 28;8:630888. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.630888. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 33732684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The CUL4B-based E3 ubiquitin ligase regulates mitosis and brain development by recruiting phospho-specific DCAFs.EMBO J. 2023 Sep 4;42(17):e112847. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022112847. Epub 2023 Jun 27. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37365982 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

