Novel Bioengineered Three-Dimensional Human Intestinal Model for Long-Term Infection of Cryptosporidium parvum
- PMID: 28052996
- PMCID: PMC5328481
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.00731-16
Novel Bioengineered Three-Dimensional Human Intestinal Model for Long-Term Infection of Cryptosporidium parvum
Abstract
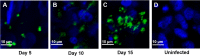
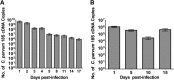
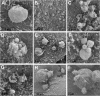
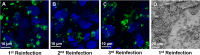
Cryptosporidium spp. are apicomplexan parasites of global importance that cause human diarrheal disease. In vitro culture models that may be used to study this parasite and that have physiological relevance to in vivo infection remain suboptimal. Thus, the pathogenesis of cryptosporidiosis remains poorly characterized, and interventions for the disease are limited. In this study, we evaluated the potential of a novel bioengineered three-dimensional (3D) human intestinal tissue model (which we developed previously) to support long-term infection by Cryptosporidium parvum Infection was assessed by immunofluorescence assays and confocal and scanning electron microscopy and quantified by quantitative reverse transcription-PCR. We found that C. parvum infected and developed in this tissue model for at least 17 days, the extent of the study time used in the present study. Contents from infected scaffolds could be transferred to fresh scaffolds to establish new infections for at least three rounds. Asexual and sexual stages and the formation of new oocysts were observed during the course of infection. Additionally, we observed ablation, blunting, or distortion of microvilli in infected epithelial cells. Ultimately, a 3D model system capable of supporting continuous Cryptosporidium infection will be a useful tool for the study of host-parasite interactions, identification of putative drug targets, screening of potential interventions, and propagation of genetically modified parasites.
Keywords: 3D model; Cryptosporidium; in vitro culture; intestinal epithelial cells.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures




References
-
- Checkley W, White AC Jr, Jaganath D, Arrowood MJ, Chalmers RM, Chen X, Fayer R, Griffiths JK, Guerrant RL, Hedstrom L, Huston CD, Kotloff KL, Kang G, Mead JR, Miller M, Petri WA Jr, Priest JW, Roos DS, Striepen B, Thompson RC, Ward HD, Van Voorhis WA, Xiao L, Zhu G, Houpt ER. 2015. A review of the global burden, novel diagnostics, therapeutics, and vaccine targets for cryptosporidium. Lancet Infect Dis 15:85–94. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70772-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kotloff KL, Nataro JP, Blackwelder WC, Nasrin D, Farag TH, Panchalingam S, Wu Y, Sow SO, Sur D, Breiman RF, Faruque ASG, Zaidi AKM, Saha D, Alonso PL, Tamboura B, Sanogo D, Onwuchekwa U, Manna B, Ramamurthy T, Kanungo S, Ochieng JB, Omore R, Oundo JO, Hossain A, Das SK, Ahmed S, Qureshi S, Quadri F, Adegbola RA, Antonio M, Hossain MJ, Akinsola A, Mandomando I, Nhampossa T, Acácio S, Biswas K, O'Reilly CE, Mintz ED, Berkeley LY, Muhsen K, Sommerfelt H, Robins-Browne RM, Levine MM. 2013. Burden and aetiology of diarrhoeal disease in infants and young children in developing countries (the Global Enteric Multicenter Study, GEMS): a prospective, case-control study. Lancet 382:209–222. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60844-2. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

